The Antimicrobial Testing Leadership and Surveillance (ATLAS) global surveillance program collected clinical isolates of Enterobacterales (n = 8416) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (n = 2521) from 41 medical centers in 10 Latin American countries from 2017 to 2019. In vitro activities of ceftazidime-avibactam and comparators were determined using the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) broth microdilution method. Overall, 98.1% of Enterobacterales and 86.9% of P. aeruginosa isolates were susceptible to ceftazidime-avibactam. When isolates were analyzed by country of origin, susceptibility to ceftazidime-avibactam for Enterobacterales ranged from 97.8% to 100% for nine of 10 countries (except Guatemala, 86.3% susceptible) and from 75.9% to 98.4% for P. aeruginosa in all 10 countries. For Enterobacterales, 100% of AmpC-positive, ESBL- and AmpC-positive, GES-type carbapenemase-positive, and OXA-48-like-positive isolates were ceftazidime-avibactam-susceptible as were 99.8%, 91.8%, and 74.7% of ESBL-positive, multidrug-resistant (MDR), and meropenem-nonsusceptible isolates. Among meropenem-nonsusceptible isolates of Enterobacterales, 24.4% (139/570) carried a metallo-β-lactamase (MBL); 83.3% of the remaining meropenem-nonsusceptible isolates carried another class of carbapenemase and 99.4% of those isolates were ceftazidime-avibactam-susceptible. Among meropenem-non-susceptible isolates of P. aeruginosa (n = 835), 25.6% carried MBLs; no acquired β-lactamase was identified in the majority of isolates (64.8%; 87.2% of those isolates were ceftazidime-avibactam-susceptible). Overall, clinical isolates of Enterobacterales collected in Latin America from 2017 to 2019 were highly susceptible to ceftazidime-avibactam, including isolates carrying ESBLs, AmpCs, and KPCs. Country-specific variation in susceptibility to ceftazidime-avibactam was more common among isolates of P. aeruginosa than Enterobacterales. The frequency of MBL-producers among Enterobacterales from Latin America was low (1.7% of all isolates; 146/8,416), but higher than reported in previous surveillance studies.
Ceftazidime-avibactam combines ceftazidime, an established third-generation cephalosporin, with avibactam, a diazabicyclooctanone non-β-lactam β-lactamase inhibitor, and is indicated in the treatment of patients with complicated urinary tract infections, including pyelonephritis, complicated intra-abdominal infections, and hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia caused by gram-negative bacilli, including species of Enterobacterales and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.1In vitro, avibactam has consistently demonstrated the ability to restore the potency of ceftazidime against isolates of Gram-negative bacilli carrying Ambler class A β-lactamases (including extended spectrum β-lactamases [ESBLs] and KPC carbapenemases), class C β-lactamases (AmpC cephalosporinases), and some class D β-lactamases (OXA-48-like carbapenemases), including isolates harboring ESBL and AmpC enzymes in combination with impaired permeability due to porin mutation or loss.2–6 Ceftazidime-avibactam is not active against isolates of Enterobacterales and P. aeruginosa carrying class B metallo-β-lactamases (MBLs) (e.g., NDM, IMP, VIM) and rare isolates that possess specific protein sequence mutations in target enzymes (AmpC, KPC, PBP3) or overexpress certain efflux pumps due to mutation.2–4,5–18
Carbapenemase-producing gram-negative bacilli are of increasing global concern as carbapenems are recommended in the treatment of patients with severe infections due to ESBL- and AmpC-producing Gram-negative bacilli. Carbapenemase-producing Gram-negative bacilli frequently demonstrate a multidrug-resistant (MDR) phenotype leaving few therapeutic options and are associated with elevated patient morbidity and mortality.2,3 Ceftazidime-avibactam may be an appropriate agent for treatment of some patients with infections caused by Enterobacterales or P. aeruginosa when treatment options are limited.
The intent of the current study was to provide data on the in vitro activities of ceftazidime-avibactam and comparators tested against clinical isolates of Enterobacterales and P. aeruginosa collected from hospitalized patients in 10 Latin American countries over a recent three-year time period (2017–2019). In addition, we sought to analyze the activity of ceftazidime-avibactam against carbapenem-nonsusceptible, MDR, and molecularly characterized β-lactamase-producing isolate subsets. These data were collected as part of the Antimicrobial Testing Leadership and Surveillance (ATLAS) global surveillance program, which succeeded the International Network for Optimal Resistance Monitoring (INFORM) global surveillance program and continues its framework and mission. The INFORM program was established in 2012 to benchmark and then monitor the in vitro activity of ceftazidime-avibactam and comparative agents against clinical isolates of β-lactamase-producing Enterobacterales and non-fermentative Gram-negative bacilli, including P. aeruginosa. The current study extends earlier publications on isolates collected in Latin America from 2012 to 2017 under the INFORM program.2,3 Only a limited number of other, now outdated, surveillance studies to determine rates of antimicrobial resistance in clinical isolates from patients in Latin American countries have been published.19–23 To date, the majority of other published studies have not included β-lactamase characterization of resistant isolates from the Latin America region and generally have not provided country-specific ceftazidime-avibactam susceptibility data for Gram-negative bacilli isolated from patients in as many Latin America countries as the current study of ATLAS surveillance program data.2,3,19–23
Materials and methodsClinical isolates of Enterobacterales and P. aeruginosaThe ATLAS global surveillance program collected 10937 non-duplicate clinical isolates of Gram-negative bacilli (8416 isolates of Enterobacterales and 2521 isolates of P. aeruginosa) from 41 medical center laboratories in 10 countries in Latin America from 2017 to 2019. The ATLAS program annually requests that each participating medical center laboratory collect pre-defined quotas of selected bacterial pathogens isolated from patients with specific types of infection.2,3 Collection was limited to one isolate per patient. All isolates were determined to be clinically significant by participating laboratory algorithms and were collected irrespective of antimicrobial susceptibility profile.2,3 The demographic information associated with the 10937 isolates is summarized in supplementary Table S1. All isolates were transported to IHMA (Schaumburg, IL, USA) which served as the central testing laboratory for the ATLAS program. IHMA confirmed the identity of each isolate using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry (Bruker Daltonics, Billerica, MA, USA) prior to antimicrobial susceptibility testing.
Antimicrobial susceptibility testingAntimicrobial susceptibility testing was performed following the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) standard method using custom 96-well broth microdilution panels prepared by Trek (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Oakwood Village, OH, USA; 2017) or IHMA (2018–2019).24,25 Ceftazidime-avibactam was tested using a fixed concentration of 4 µg/ml of avibactam.24 MICs were interpreted using 2020 CLSI breakpoints24 with the exception of tigecycline which used current US FDA MIC interpretative breakpoints.26
An MDR phenotype was defined as resistance to sentinel agents from three or more antimicrobial agent classes, including cephalosporins (cefepime), monobactams (aztreonam), β-lactam-β-lactamase inhibitor combinations (piperacillin-tazobactam), carbapenems (meropenem), fluoroquinolones (levofloxacin), aminoglycosides (amikacin), and polymyxins (colistin).
Screening of clinical isolates of Enterobacterales and P. aeruginosa for β-lactamase genesAll isolates of Enterobacterales testing with MICs to meropenem of ≥2 µg/ml and all E. coli, K. pneumoniae, K. oxytoca and P. mirabilis with MICs to ceftazidime or aztreonam of ≥2 µg/ml were screened for β-lactamase content using published multiplex PCR assays.27 These assays detected genes encoding carbapenemases (KPC, GES, NDM, IMP, VIM, SPM, GIM, OXA-48-like), ESBLs (TEM, SHV, CTX-M, VEB, PER, GES), original (narrow)-spectrum β-lactamases (TEM and SHV enzymes lacking substitutions at amino acid positions 104, 164, or 238 in TEM or 146, 238, or 240 in SHV that are associated with ESBL activity),28 and plasmid-mediated AmpC β-lactamases (ACC, ACT, CMY, DHA, FOX, MIR, MOX) as previously described.27 All isolates of P. aeruginosa testing with MICs to meropenem of ≥4 µg/ml were screened for genes encoding the β-lactamases listed above and OXA-24/40-like carbapenemases, as described previously.3 Enzyme variants were identified by amplification of full-length β-lactamase genes followed by DNA sequencing and comparison of the sequences generated to the National Center for Biotechnology Information database (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov).
ResultsOf the 8416 isolates of Enterobacterales tested, 98.1% were susceptible to ceftazidime-avibactam (MIC90, 0.5 µg/ml) (Table 1). Percent susceptible values for all other agents tested were comparable (tigecycline, amikacin) or lower than for ceftazidime-avibactam. Among the 6.8% of isolates that tested as meropenem-nonsusceptible, which included 139 MBL-positive isolates, 74.7% were susceptible to ceftazidime-avibactam. When MBL-positive isolates were removed from the subset of meropenem-nonsusceptible isolates, susceptibility to ceftazidime-avibactam increased to 99.4% among isolates that were serine carbapenemase-positive and 95.8% among isolates that were meropenem-nonsusceptible and carbapenemase-negative. Of the subset of isolates identified with an MDR phenotype, which included MBL-positive isolates, 91.8% were susceptible to ceftazidime-avibactam.
In vitro activity of ceftazidime-avibactam and comparator agents against Enterobacterales isolates collected in the Latin American region as part of the ATLAS global surveillance program from 2017 to 2019.
| Antimicrobial agent | MIC (µg/ml) | Interpretation (CLSI) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organism, phenotype/genotype (no. of isolates) | MIC50 | MIC90 | % Susceptible | % Intermediate | % Resistant | |
| Latin America, All Enterobacterales (8416)a | Ceftazidime-avibactam | 0.12 | 0.5 | 98.1 | NA | 1.9 |
| Ceftazidime | 0.25 | 64 | 67.8 | 3.6 | 28.5 | |
| Cefepime | ≤0.12 | >16 | 68.5 | 6.7 | 24.7 | |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 2 | >64 | 82.7 | 5.4 | 11.9 | |
| Meropenem | ≤0.06 | 0.12 | 93.2 | 0.8 | 6.0 | |
| Levofloxacin (n = 8415)d | ≤0.25 | >8 | 61.0 | 5.6 | 33.4 | |
| Amikacin | 2 | 8 | 96.2 | 1.5 | 2.3 | |
| Colistin | 0.5 | >8 | NA | 81.1 | 18.9 | |
| Tigecycline | 0.5 | 1 | 97.2 | 2.4 | 0.4 | |
| Meropenem-NS (570)b | Ceftazidime-avibactam | 1 | >128 | 74.7 | NA | 25.3 |
| Ceftazidime | 128 | >128 | 5.4 | 3.9 | 90.7 | |
| Cefepime | >16 | >16 | 3.7 | 7.7 | 88.6 | |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | >64 | >64 | 1.9 | 5.6 | 92.5 | |
| Meropenem | >8 | >8 | 0 | 11.6 | 88.4 | |
| Levofloxacin | >8 | >8 | 16.0 | 8.4 | 75.6 | |
| Amikacin | 8 | >32 | 70.2 | 10.4 | 19.5 | |
| Colistin | 0.5 | >8 | NA | 78.2 | 21.8 | |
| Tigecycline | 0.5 | 2 | 95.6 | 4.0 | 0.4 | |
| Meropenem-NS, MBL-, carbapenemase+ (358) | Ceftazidime-avibactam | 1 | 2 | 99.4 | NA | 0.6 |
| Ceftazidime | 64 | >128 | 5.3 | 5.6 | 89.1 | |
| Cefepime | >16 | >16 | 4.5 | 8.4 | 87.2 | |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | >64 | >64 | 0 | 3.4 | 96.6 | |
| Meropenem | >8 | >8 | 0 | 7.0 | 93.0 | |
| Levofloxacin | >8 | >8 | 14.2 | 5.0 | 80.7 | |
| Amikacin | 4 | >32 | 76.5 | 13.1 | 10.3 | |
| Colistin | 0.5 | >8 | NA | 74.9 | 25.1 | |
| Tigecycline | 0.5 | 2 | 98.0 | 1.7 | 0.3 | |
| Meropenem-NS, MBL-, carbapenemase- (72) | Ceftazidime-avibactam | 1 | 4 | 95.8 | NA | 4.2 |
| Ceftazidime | 64 | >128 | 16.7 | 2.8 | 80.6 | |
| Cefepime | >16 | >16 | 6.9 | 8.3 | 84.7 | |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | >64 | >64 | 11.1 | 15.3 | 73.6 | |
| Meropenem | 2 | >8 | 0 | 52.8 | 47.2 | |
| Levofloxacin | >8 | >8 | 19.4 | 9.7 | 70.8 | |
| Amikacin | 4 | >32 | 81.9 | 2.8 | 15.3 | |
| Colistin | 0.5 | >8 | NA | 87.5 | 12.5 | |
| Tigecycline | 0.5 | 2 | 91.7 | 8.3 | 0 | |
| Multidrug-resistant (1773)c | Ceftazidime-avibactam | 0.5 | 4 | 91.8 | NA | 8.2 |
| Ceftazidime | 64 | >128 | 5.4 | 4.7 | 89.9 | |
| Cefepime | >16 | >16 | 1.6 | 3.6 | 94.8 | |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 32 | >64 | 44.3 | 11.1 | 44.6 | |
| Meropenem | ≤0.06 | >8 | 69.4 | 2.6 | 28.0 | |
| Levofloxacin (n = 1772)d | >8 | >8 | 7.1 | 4.3 | 88.5 | |
| Amikacin | 4 | >32 | 84.2 | 5.5 | 10.3 | |
| Colistin | 0.5 | >8 | NA | 85.4 | 14.6 | |
| Tigecycline | 0.5 | 2 | 95.8 | 3.5 | 0.7 | |
Abbreviations: NS, non-susceptible; MBL-, no gene encoding a metallo-β-lactamase was detected by PCR; carbapenemase+/-, a gene encoding a serine carbapenemase was (+) or was not (-) detected by PCR; multidrug-resistant, isolates resistant to three or more sentinel agents from different antimicrobial classes; NA, no breakpoint available.
All Enterobacterales were composed of Citrobacter amalonaticus (n = 10), Citrobacter braakii (n = 20), Citrobacter farmeri (n = 7), Citrobacter freundii (n = 251), Citrobacter koseri (n = 119), Citrobacter sedlakii (n = 6), Citrobacter youngae (n = 1), Citrobacter sp. (n = 4), Enterobacter asburiae (n = 87), Enterobacter bugandensis (n = 8), Enterobacter cloacae (n = 703), Enterobacter cloacae complex (n = 25), Enterobacter kobei (n = 27), Enterobacter ludwigii (n = 4), Enterobacter xiangfangensis (n = 14), Enterobacter sp. (n = 32), Escherichia coli (n = 2747), Klebsiella aerogenes (n = 221), Klebsiella oxytoca (n = 213), Klebsiella pneumoniae (n = 2441), Klebsiella variicola (n = 98), Morganella morganii (n = 263), Pantoea agglomerans (n = 1), Pantoea septica (n = 1), Proteus hauseri (n = 48), Proteus mirabilis (n = 436), Proteus penneri (n = 8), Proteus vulgaris (n = 58), Proteus sp. (n = 2), Providencia alcalifaciens (n = 4), Providencia rettgeri (n = 51), Providencia stuartii (n = 83), Providencia sp. (n = 2), Raoultella ornithinolytica (n = 17), Raoultella planticola (n = 2), Raoultella terrigena (n = 1), Salmonella sp. (n = 1), Serratia liquefaciens (n = 3), Serratia marcescens (n = 392), Serratia rubidaea (n = 1), Serratia ureilytica (n = 2), and Serratia sp. (n = 2).
One meropenem-nonsusceptible isolate collected in Guatemala was not molecularly characterized for β-lactamase genes.
Multidrug resistant Enterobacterales were composed of Citrobacter freundii (n = 15), Citrobacter koseri (n = 2), Enterobacter asburiae (n = 11), Enterobacter cloacae (n = 123), Enterobacter cloacae complex (n = 2), Enterobacter xiangfangensis (n = 1), Enterobacter sp. (n = 2), Escherichia coli (n = 605), Klebsiella aerogenes (n = 12), Klebsiella oxytoca (n = 14), Klebsiella pneumoniae (n = 845), Klebsiella variicola (n = 5), Morganella morganii (n = 18), Proteus mirabilis (n = 39), Providencia rettgeri (n = 7), Providencia stuartii (n = 17), Raoultella ornithinolytica (n = 1), Salmonella sp. (n = 1), and Serratia marcescens (n = 53).
Percent susceptible values for ceftazidime-avibactam for all Enterobacterales isolates collected from nine of the 10 countries surveyed ranged from 97.8% (Venezuela) to 100% (Chile, Dominican Republic) (Table 2). Enterobacterales from Guatemala were exceptional in that only 86.3% of isolates were susceptible to ceftazidime-avibactam. The percentages of isolates that tested as non-susceptible to meropenem differed by almost 15% among the 10 Latin American countries surveyed, ranging from 0% in Dominican Republic and 0.9% in Panama to 14.8% in Guatemala. Among meropenem-nonsusceptible isolates, susceptibility to ceftazidime-avibactam ranged from 100% (Chile) to 0% (Costa Rica, n = 3) and was >87% for four countries, ∼50–67% for three countries, and <10% for two countries. When MBL-positive isolates were removed from the dataset, susceptibility to ceftazidime-avibactam increased to ≥98.8%, exceeding susceptibility to all other agents tested, for meropenem-nonsusceptible isolates collected in all Latin American countries except Guatemala (66.7% susceptible, n = 6) and Mexico (92.9% susceptible among meropenem-nonsusceptible, carbapenemase-negative isolates). Country-specific MDR rates among Enterobacterales isolates ranged from 8.1% (Costa Rica) to 26.9% (Guatemala), with ≥93.5% of MDR isolates collected in seven countries testing as susceptible to ceftazidime-avibactam; susceptibilities of MDR isolates were lower in Venezuela (88.0%), Costa Rica (80.0%), and Guatemala (49.0%).
Percentages of Enterobacterales isolates collected in ten Latin American countries as part of the ATLAS global surveillance program from 2017 to 2019 that were susceptible to ceftazidime-avibactam and comparator agents.
| Country | Antimicrobial agent | Phenotype/genotype | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (no. of isolates) | |||||||
| % Susceptible (CLSI) | |||||||
| All isolates | Meropenem-NS | Meropenem-NS, MBL-, All | Meropenem-NS, MBL-, carbapenemase+ | Meropenem-NS, MBL-, carbapenemase- | Multidrug-resistant | ||
| Argentina | (1039) | (87) | (81)a | (212) | |||
| Ceftazidime-avibactam | 98.8 | 92.0 | 98.8 | 96.7 | |||
| Ceftazidime | 71.7 | 2.3 | 2.5 | 6.6 | |||
| Cefepime | 73.1 | 2.3 | 2.5 | 1.4 | |||
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 79.1 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 23.1 | |||
| Meropenem | 91.6 | 0 | 0 | 59.9 | |||
| Levofloxacin | 61.0 | 9.2 | 9.9 | 7.1 | |||
| Amikacin | 94.8 | 65.5 | 69.1 | 76.9 | |||
| Colistin | NA | NA | NA | NA | |||
| Tigecycline | 96.8 | 97.7 | 98.8 | 96.2 | |||
| Brazil | (1646) | (202) | (164) | (14) | (400) | ||
| Ceftazidime-avibactam | 98.4 | 87.6 | 99.4 | 100 | 93.5 | ||
| Ceftazidime | 71.7 | 5.0 | 4.9 | 14.3 | 9.0 | ||
| Cefepime | 69.3 | 1.5 | 1.8 | 0 | 2.0 | ||
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 78.0 | 0.5 | 0 | 7.1 | 24.3 | ||
| Meropenem | 87.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50.2 | ||
| Levofloxacin | 61.8 | 10.9 | 9.8 | 14.3 | 6.8 | ||
| Amikacin | 96.5 | 79.7 | 80.5 | 78.6 | 86.5 | ||
| Colistin | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | ||
| Tigecycline | 97.5 | 97.0 | 97.6 | 92.9 | 95.5 | ||
| Chile | (805) | (22) | (22)b | (157) | |||
| Ceftazidime-avibactam | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |||
| Ceftazidime | 67.2 | 0 | 0 | 10.2 | |||
| Cefepime | 69.3 | 0 | 0 | 1.9 | |||
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 84.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 52.9 | |||
| Meropenem | 97.3 | 0 | 0 | 86.0 | |||
| Levofloxacin | 67.2 | 0 | 0 | 3.2 | |||
| Amikacin | 96.8 | 95.5 | 95.5 | 86.0 | |||
| Colistin | NA | NA | NA | NA | |||
| Tigecycline | 97.4 | 90.9 | 90.9 | 95.5 | |||
| Colombia | (1252) | (107) | (83) | (12) | (209) | ||
| Ceftazidime-avibactam | 98.9 | 89.7 | 100 | 100 | 94.7 | ||
| Ceftazidime | 72.1 | 13.1 | 12.0 | 33.3 | 5.3 | ||
| Cefepime | 71.7 | 10.3 | 10.8 | 16.7 | 2.9 | ||
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 80.8 | 0.9 | 0 | 8.3 | 34.0 | ||
| Meropenem | 91.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 55.0 | ||
| Levofloxacin | 67.3 | 31.8 | 27.7 | 58.3 | 17.2 | ||
| Amikacin | 96.2 | 71.0 | 71.1 | 83.3 | 81.8 | ||
| Colistin | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | ||
| Tigecycline | 97.0 | 95.3 | 97.6 | 75.0 | 95.2 | ||
| Costa Rica | (185) | (3)c | (15) | ||||
| Ceftazidime-avibactam | 98.4 | 0 | 80.0 | ||||
| Ceftazidime | 75.7 | 0 | 6.7 | ||||
| Cefepime | 85.4 | 0 | 13.3 | ||||
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 88.6 | 0 | 53.3 | ||||
| Meropenem | 98.4 | 0 | 80.0 | ||||
| Levofloxacin | 83.2 | 0 | 6.7 | ||||
| Amikacin | 98.9 | 33.3 | 86.7 | ||||
| Colistin | NA | NA | NA | ||||
| Tigecycline | 99.5 | 100 | 100 | ||||
| Dominican Republic | (193)d | (28) | |||||
| Ceftazidime-avibactam | 100 | 100 | |||||
| Ceftazidime | 75.1 | 14.3 | |||||
| Cefepime | 75.6 | 0.0 | |||||
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 95.3 | 78.6 | |||||
| Meropenem | 100 | 100 | |||||
| Levofloxacin | 51.3 | 0.0 | |||||
| Amikacin | 96.4 | 85.7 | |||||
| Colistin | NA | NA | |||||
| Tigecycline | 97.9 | 96.4 | |||||
| Guatemala | (364) | (54)e | (6)f | (98) | |||
| Ceftazidime-avibactam | 86.3 | 7.4 | 66.7 | 49.0 | |||
| Ceftazidime | 58.2 | 1.9 | 16.7 | 2.0 | |||
| Cefepime | 58.2 | 5.6 | 50.0 | 1.0 | |||
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 73.4 | 1.9 | 0.0 | 33.7 | |||
| Meropenem | 85.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 49.0 | |||
| Levofloxacin | 54.9 | 22.2 | 50.0 | 10.2 | |||
| Amikacin | 90.7 | 46.3 | 66.7 | 69.4 | |||
| Colistin | NA | NA | NA | NA | |||
| Tigecycline | 99.2 | 98.1 | 100 | 99.0 | |||
| Mexico | (1802) | (59) | (16) | (14) | (460) | ||
| Ceftazidime-avibactam | 98.2 | 49.2 | 100 | 92.9 | 93.7 | ||
| Ceftazidime | 55.3 | 6.8 | 6.3 | 21.4 | 1.3 | ||
| Cefepime | 57.8 | 3.4 | 6.3 | 7.1 | 0.7 | ||
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 86.2 | 10.2 | 0 | 28.6 | 67.8 | ||
| Meropenem | 96.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 88.0 | ||
| Levofloxacin | 55.3 | 18.6 | 18.8 | 14.3 | 3.9 | ||
| Amikacin | 96.7 | 67.8 | 100 | 85.7 | 88.9 | ||
| Colistin | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | ||
| Tigecycline | 96.6 | 86.4 | 100 | 100 | 95.0 | ||
| Panama | (316) | (3) | (2)g | (44) | |||
| Ceftazidime-avibactam | 99.7 | 66.7 | 100 | 97.7 | |||
| Ceftazidime | 76.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Cefepime | 79.7 | 0 | 0 | 2.3 | |||
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 91.5 | 0 | 0 | 63.6 | |||
| Meropenem | 99.1 | 0 | 0 | 93.2 | |||
| Levofloxacin | 55.4 | 33.3 | 50.0 | 4.5 | |||
| Amikacin | 99.7 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |||
| Colistin | NA | NA | NA | NA | |||
| Tigecycline | 96.2 | 100 | 100 | 93.2 | |||
| Venezuela | (814) | (33) | (16)h | (150) | |||
| Ceftazidime-avibactam | 97.8 | 48.5 | 100 | 88.0 | |||
| Ceftazidime | 74.4 | 0 | 0 | 4.0 | |||
| Cefepime | 74.2 | 0 | 0 | 0.7 | |||
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 87.1 | 0 | 0 | 55.3 | |||
| Meropenem | 95.9 | 0 | 0 | 78.7 | |||
| Levofloxacin (n = 813)i | 58.8 | 9.1 | 0 | 8.1 | |||
| Amikacin | 95.9 | 48.5 | 62.5 | 80.0 | |||
| Colistin | NA | NA | NA | NA | |||
| Tigecycline | 97.2 | 97.0 | 100 | 98.0 | |||
Abbreviations: NS, non-susceptible; MBL-, no gene encoding a metallo-β-lactamase was detected by PCR; carbapenemase+/-, a gene encoding a serine carbapenemase was (+) or was not (-) detected by PCR; multidrug-resistant, isolates resistant to three or more sentinel agents from different drug classes; NA, no breakpoint available.
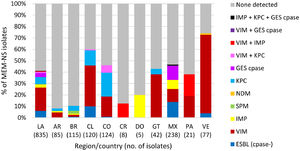
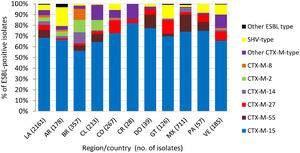
One or more β-lactamase genes were detected in 2512 of 2578 Enterobacterales isolates screened for β-lactamase content (Methods). A total of 2254 ESBLs were detected singly or in combination with other β-lactamases in 2161 isolates, with CTX-M-15 identified in >50% of ESBL-positive isolates in each Latin American country and in 71.5% (1545/2161) of ESBL-positive isolates overall (Fig. 1). Similarly, 519 genes encoding carbapenemases were identified in 497 of 569 meropenem-nonsusceptible Enterobacterales isolates (one meropenem-nonsusceptible isolate collected in Guatemala was not molecularly characterized for β-lactamase genes). KPC was the most common carbapenemase identified in meropenem-nonsusceptible molecularly characterized isolates overall, accounting for 61.5% (350/569) of isolates, and isolates carrying KPC as the sole carbapenemase composed the majority in Argentina (89.7%), Brazil (81.7%), Colombia (77.6%), and Panama (66.7%) (Fig. 2). NDM (an MBL) was the second most common carbapenemase identified in the region and was found alone or with serine carbapenemases in 100%, 86.8%, 48.5%, and 47.5% of meropenem-nonsusceptible isolates collected in Costa Rica (n = 3), Guatemala, Venezuela, and Mexico, respectively.
Extended-spectrum β-lactamases identified in Enterobacterales isolates collected in ten Latin American countries as part of the ATLAS global surveillance program from 2017 to 2019LA, Latin America; AR, Argentina; BR, Brazil; CL, Chile; CO, Colombia; CR, Costa Rica; DO, Dominican Republic; GT, Guatemala; MX, Mexico; PA, Panama; VE, Venezuela; ESBL-positive, one or more genes encoding an extended-spectrum β-lactamase was detected by PCR. ESBL-positive isolates included meropenem-susceptible and meropenem-nonsusceptible isolates, some of which carried multiple ESBLs or additional β-lactamases (e.g. original (narrow)-spectrum β-lactamases, AmpC β-lactamases, serine carbapenemases, and/or metallo-β-lactamases). Isolates carrying multiple ESBLs were counted for each individual ESBL type.
β-lactamases identified in meropenem-nonsusceptible Enterobacterales isolates collected in ten Latin American countries as part of the ATLAS global surveillance program from 2017 to 2019LA, Latin America; AR, Argentina; BR, Brazil; CL, Chile; CO, Colombia; CR, Costa Rica; GT, Guatemala; MX, Mexico; PA, Panama; VE, Venezuela; Cpase, carbapenemase; ESBL, extended-spectrum β-lactamase; None detected, no gene encoding an acquired β-lactamase was detected by PCR. ESBL (cpase-) included isolates carrying CTX-M-type [CTX-M-15 (n = 28), CTX-M-2 (n = 8), CTX-M-15 and CTX-M-2 or TEM-type ESBL (n = 7), CTX-M-1 group (n = 7), CTX-M-8 (n = 1)] and SHV-type (n = 1) ESBLs that were assumed to harbor permeability defects. One meropenem-nonsusceptible (MEM-NS) isolate collected in Guatemala was not molecularly characterized for β-lactamase genes. No MEM-NS Enterobacterales isolates were collected in the Dominican Republic during the surveyed time period.
Table 3 depicts the in vitro activity of ceftazidime-avibactam and comparator agents against isolates of Enterobacterales molecularly characterized for β-lactamase gene content. Ceftazidime-avibactam inhibited 100% of AmpC-positive, ESBL- and AmpC-positive, GES-type carbapenemase-positive, and OXA-48-like-positive isolates of Enterobacterales as well as 99.8% of ESBL-positive isolates. Percentages of susceptibility to ceftazidime-avibactam were similar to or greater than observed for other β-lactams, including meropenem (95.7–100% susceptible) and piperacillin tazobactam (56.5–85.7% susceptible), among ESBL-positive, AmpC-positive, and ESBL- and AmpC-positive isolates. The activities of all β-lactams tested were significantly reduced compared to ceftazidime-avibactam against KPC-positive (2.5–9.1% susceptible) and OXA-48-like-positive (0–37.0% susceptible) isolates. As anticipated, ceftazidime-avibactam, similar to all other β-lactams, was poorly active against isolates carrying MBLs; only tigecycline retained in vitro activity against >50% of MBL-positive isolates.
In vitro activity of ceftazidime-avibactam and comparator agents against β-lactamase-positive Enterobacterales isolates collected in the Latin American region as part of the ATLAS global surveillance program from 2017-2019.
| Organism, phenotype/genotype (no. of isolates) | Antimicrobial agent | MIC (µg/ml) | Interpretation (CLSI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC50 | MIC90 | % Susceptible | % Intermediate | % Resistant | ||
| ESBL-positive (1816)a | Ceftazidime-avibactam | 0.25 | 0.5 | 99.8 | NA | 0.2 |
| Ceftazidime | 32 | 128 | 13.1 | 11.2 | 75.7 | |
| Cefepime | >16 | >16 | 4.4 | 20.2 | 75.4 | |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 8 | >64 | 76.0 | 11.7 | 12.3 | |
| Meropenem | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 97.3 | 1.8 | 0.9 | |
| Levofloxacin | >8 | >8 | 18.9 | 10.2 | 70.8 | |
| Amikacin | 4 | 8 | 95.1 | 1.9 | 3.0 | |
| Colistin | 0.5 | 1 | NA | 97.2 | 2.8 | |
| Tigecycline | 0.25 | 1 | 97.7 | 1.9 | 0.4 | |
| AmpC-positive (49)b | Ceftazidime-avibactam | 0.12 | 0.25 | 100 | NA | 0 |
| Ceftazidime | 32 | 128 | 6.1 | 16.3 | 77.6 | |
| Cefepime | 0.25 | 2 | 91.8 | 8.2 | 0.0 | |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 4 | >64 | 85.7 | 2.0 | 12.2 | |
| Meropenem | ≤0.06 | 0.12 | 100 | 0 | 0 | |
| Levofloxacin | 8 | >8 | 28.6 | 8.2 | 63.3 | |
| Amikacin | 2 | 4 | 100 | 0 | 0 | |
| Colistin | 0.25 | >8 | NA | 85.7 | 14.3 | |
| Tigecycline | 0.25 | 1 | 95.9 | 2.0 | 2.0 | |
| ESBL-positive + AmpC-positive (23)c | Ceftazidime-avibactam | 0.25 | 2 | 100 | NA | 0 |
| Ceftazidime | 64 | >128 | 0 | 8.7 | 91.3 | |
| Cefepime | >16 | >16 | 8.7 | 13.0 | 78.3 | |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 16 | >64 | 56.5 | 17.4 | 26.1 | |
| Meropenem | ≤0.06 | 0.25 | 95.7 | 0 | 4.3 | |
| Levofloxacin | >8 | >8 | 21.7 | 8.7 | 69.6 | |
| Amikacin | 2 | 8 | 91.3 | 0 | 8.7 | |
| Colistin | 0.25 | 0.5 | NA | 95.7 | 4.3 | |
| Tigecycline | 0.25 | 1 | 95.7 | 4.3 | 0 | |
| KPC-positive (364)d | Ceftazidime-avibactam | 0.5 | 2 | 99.5 | NA | 0.5 |
| Ceftazidime | 64 | >128 | 9.1 | 5.8 | 85.2 | |
| Cefepime | >16 | >16 | 7.7 | 9.3 | 83.0 | |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | >64 | >64 | 2.5 | 5.8 | 91.8 | |
| Meropenem | >8 | >8 | 6.3 | 5.5 | 88.2 | |
| Levofloxacin | >8 | >8 | 16.5 | 6.6 | 76.9 | |
| Amikacin | 4 | >32 | 76.9 | 12.9 | 10.2 | |
| Colistin | 0.5 | >8 | NA | 75.3 | 24.7 | |
| Tigecycline | 0.5 | 2 | 97.8 | 1.9 | 0.3 | |
| GES-type carbapenemase-positive (5)e | Ceftazidime-avibactam | – | – | 100 | NA | 0 |
| Ceftazidime | – | – | 0 | 0 | 100 | |
| Cefepime | – | – | 40.0 | 60.0 | 0 | |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | – | – | 20.0 | 20.0 | 60.0 | |
| Meropenem | – | – | 100 | 0 | 0 | |
| Levofloxacin | – | – | 60.0 | 40.0 | 0 | |
| Amikacin | – | – | 40.0 | 60.0 | 0 | |
| Colistin | – | – | NA | 100 | 0 | |
| Tigecycline | – | – | 100 | 0 | 0 | |
| OXA-48-like-positive (27)f | Ceftazidime-avibactam | 0.5 | 1 | 100 | NA | 0 |
| Ceftazidime | 64 | >128 | 7.4 | 0 | 92.6 | |
| Cefepime | >16 | >16 | 14.8 | 0 | 85.2 | |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | >64 | >64 | 0 | 7.4 | 92.6 | |
| Meropenem | 2 | >8 | 37.0 | 18.5 | 44.4 | |
| Levofloxacin | >8 | >8 | 18.5 | 7.4 | 74.1 | |
| Amikacin | 2 | 16 | 96.3 | 3.7 | 0 | |
| Colistin | 0.5 | 1 | NA | 100 | 0 | |
| Tigecycline | 1 | 2 | 100 | 0 | 0 | |
| MBL-positive (146)g | Ceftazidime-avibactam | >128 | >128 | 1.4 | NA | 98.6 |
| Ceftazidime | >128 | >128 | 0 | 0 | 100 | |
| Cefepime | >16 | >16 | 0 | 8.2 | 91.8 | |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | >64 | >64 | 2.7 | 8.2 | 89.0 | |
| Meropenem | >8 | >8 | 4.8 | 2.1 | 93.2 | |
| Levofloxacin | 8 | >8 | 21.9 | 15.8 | 62.3 | |
| Amikacin | 32 | >32 | 49.3 | 6.8 | 43.8 | |
| Colistin | 0.5 | >8 | NA | 82.9 | 17.1 | |
| Tigecycline | 0.5 | 2 | 91.8 | 7.5 | 0.7 | |
ESBL-positive, isolates in which one or more acquired β-lactamase genes encoding an ESBL was detected by PCR; includes isolates that co-carry original (narrow) spectrum β-lactamases but does not include isolates that co-carry AmpC β-lactamases or KPC, GES-type, OXA-48-like or MBL carbapenemases.
AmpC-positive, isolates in which an acquired β-lactamase gene encoding an AmpC β-lactamase was detected by PCR; includes isolates that co-carry original (narrow) spectrum β-lactamases but does not include isolates that co-carry other serine β-lactamases or MBLs.
ESBL-positive and AmpC-positive, isolates in which acquired β-lactamase genes encoding ESBL and AmpC β-lactamases were detected by PCR; includes isolates that co-carry original (narrow) spectrum β-lactamases but does not include isolates that co-carry serine carbapenemases or MBLs.
KPC-positive, isolates in which a gene encoding a KPC carbapenemase was detected by PCR; includes isolates that co-carry other serine β-lactamases (including one isolate that co-carried KPC-2 and OXA-48) but does not include isolates that co-carry MBLs.
GES-type carbapenemase-positive, isolates in which a gene encoding GES-20 was detected by PCR; includes isolates that co-carry original (narrow) spectrum β-lactamases but does not include isolates that co-carry other serine β-lactamases or MBLs.
OXA-48-like positive, isolates in which a gene encoding an OXA-48-like enzyme (OXA-48, OXA-181, OXA-232, OXA-163, OXA-370) was detected by PCR; includes isolates that co-carry original (narrow) spectrum β-lactamases or ESBLs but does not include isolates that co-carry AmpC, GES-type or KPC serine β-lactamases or MBLs.
MBL-positive, isolates in which a gene encoding an NDM-type, IMP-type or VIM-type MBL was detected by PCR; includes isolates that co-carry serine β-lactamases (original (narrow) spectrum β-lactamases, ESBLs, AmpC β-lactamases, GES-type, KPC, and OXA-48-like β-lactamases) and one isolate that carried two MBLs (IMP-27 and NDM-1).
Of the 2521 P. aeruginosa isolates collected in Latin America from 2017 to 2019, 86.9% were susceptible to ceftazidime-avibactam (MIC90, 32 µg/ml) (Table 4). Percent susceptibilities to other tested agents ranged from 4.8% to 24.2% lower than for ceftazidime-avibactam, with 71.5% of isolates susceptible to ceftazidime alone and 66.9% testing as susceptible to meropenem. Among the subset of all meropenem-nonsusceptible isolates (n = 835, included 214 MBL-positive isolates), 61.9% of isolates were susceptible to ceftazidime-avibactam. When MBL-positive isolates were removed from the subset, susceptibility to ceftazidime-avibactam increased to 87.2% among meropenem-nonsusceptible and carbapenemase-negative isolates and was 45.0% among serine carbapenemase-positive isolates. Against MDR isolates, which included MBL-positive isolates, 49.0% of isolates were susceptible to ceftazidime-avibactam. Ceftazidime-avibactam displayed the highest percentages of susceptibility of all agents tested among all meropenem-nonsusceptible isolates, subsets of meropenem-nonsusceptible, carbapenemase-negative and MBL-negative, carbapenemase-positive isolates, and MDR isolates.
In vitro activity of ceftazidime-avibactam and comparator agents against P. aeruginosa isolates collected in the Latin American region as part of the ATLAS global surveillance program from 2017 to 2019.
Abbreviations: NS, non-susceptible; MBL-, no gene encoding a metallo-β-lactamase was detected by PCR; carbapenemase+/-, a gene encoding a serine carbapenemase was (+) or was not (-) detected by PCR; multidrug-resistant, isolates resistant to three or more sentinel agents from different drug classes; NA, no breakpoint available.
Analyzing data by country of origin, percentages of susceptibility to ceftazidime-avibactam were >87% in seven of the 10 countries surveyed, with the lowest values observed for Mexico, Chile and Venezuela (75.9–80.2% susceptible) (Table 5). The overall percentage of P. aeruginosa isolates that were meropenem non-susceptible was 33.1% (Table 4) and ranged from 7.8% (Dominican Republic) to 46.7% (Chile) (Table 5). Percentages of susceptibility of meropenem-nonsusceptible isolates to ceftazidime-avibactam were >50% in all countries except Venezuela (26.0% susceptible) and were ≥80% for isolates collected in Argentina (91.8%), Brazil (86.1%), Costa Rica (87.5%), and Dominican Republic (80.0%). A total of 23.4% of all P. aeruginosa displayed an MDR phenotype (Table 4), with percentages of MDR isolates ranging from 3.1% (Dominican Republic) to 32.7% (Chile) across the region (Table 5). Ceftazidime-avibactam was most active against MDR isolates from Argentina (88.7% susceptible; MIC90, 16 µg/ml) and Brazil (72.9% susceptible; MIC90, 64 µg/ml) and least active against MDR isolates from Venezuela, Panama, and Mexico (12.9–38.9% susceptible, MIC90, 128 - >128 µg/ml). Amikacin was the only tested comparator that displayed greater activity than ceftazidime-avibactam in some countries.
Percentages of P. aeruginosa isolates collected in ten Latin American countries as part of the ATLAS global surveillance program from 2017 to 2019 that were susceptible to ceftazidime-avibactam and comparator agents.
| Country | Antimicrobial agent | Phenotype/genotype | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (no. of isolates) | |||||||
| % Susceptible (CLSI) | |||||||
| All isolates | Meropenem-NS | Meropenem-NS, MBL-, All | Meropenem-NS, MBL-, carbapenemase+ | Meropenem-NS, MBL-, carbapenemase- | Multidrug-resistant | ||
| Argentina | (308) | (85) | (80)a | (71) | |||
| Ceftazidime-avibactam | 97.4 | 91.8 | 97.5 | 88.7 | |||
| Ceftazidime | 75.0 | 36.5 | 38.8 | 16.9 | |||
| Cefepime | 73.7 | 30.6 | 32.5 | 7.0 | |||
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 69.8 | 20.0 | 21.3 | 5.6 | |||
| Meropenem | 72.4 | 0 | 0 | 15.5 | |||
| Levofloxacin | 62.0 | 16.5 | 17.5 | 11.3 | |||
| Amikacin | 85.1 | 55.3 | 57.5 | 43.7 | |||
| Colistin | NA | NA | NA | NA | |||
| Brazil | (425) | (115) | (109)b | (70) | |||
| Ceftazidime-avibactam | 95.3 | 86.1 | 90.8 | 72.9 | |||
| Ceftazidime | 78.6 | 62.6 | 66.1 | 22.9 | |||
| Cefepime | 78.4 | 55.7 | 58.7 | 4.3 | |||
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 73.6 | 47.8 | 50.5 | 5.7 | |||
| Meropenem | 72.9 | 0 | 0 | 30.0 | |||
| Levofloxacin | 69.2 | 34.8 | 36.7 | 15.7 | |||
| Amikacin | 90.8 | 78.3 | 80.7 | 50.0 | |||
| Colistin | NA | NA | NA | NA | |||
| Chile | (257) | (120) | (16) | (60) | (84) | ||
| Ceftazidime-avibactam | 77.4 | 51.7 | 75.0 | 78.3 | 42.9 | ||
| Ceftazidime | 58.0 | 18.3 | 0 | 36.7 | 1.2 | ||
| Cefepime | 60.3 | 21.7 | 0 | 38.3 | 1.2 | ||
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 57.6 | 16.7 | 0 | 30.0 | 6.0 | ||
| Meropenem | 53.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.2 | ||
| Levofloxacin | 49.0 | 15.0 | 0 | 25.0 | 3.6 | ||
| Amikacin | 77.0 | 56.7 | 87.5 | 76.7 | 45.2 | ||
| Colistin | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | ||
| Colombia | (384) | (124) | (26) | (68) | (86) | ||
| Ceftazidime-avibactam | 87.5 | 62.1 | 53.8 | 92.6 | 46.5 | ||
| Ceftazidime | 71.4 | 35.5 | 0 | 63.2 | 5.8 | ||
| Cefepime | 71.9 | 33.9 | 0 | 61.8 | 1.2 | ||
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 69.3 | 29.0 | 0 | 50.0 | 5.8 | ||
| Meropenem | 67.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10.5 | ||
| Levofloxacin | 67.2 | 26.6 | 19.2 | 39.7 | 19.8 | ||
| Amikacin | 85.9 | 60.5 | 30.8 | 92.6 | 45.3 | ||
| Colistin | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | ||
| Costa Rica | (55) | (8) | (7)c | (4) | |||
| Ceftazidime-avibactam | 96.4 | 87.5 | 100 | 50.0 | |||
| Ceftazidime | 81.8 | 87.5 | 100 | 25.0 | |||
| Cefepime | 94.5 | 87.5 | 100 | 25.0 | |||
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 81.8 | 75.0 | 85.7 | 0 | |||
| Meropenem | 85.5 | 0 | 0 | 50.0 | |||
| Levofloxacin | 85.5 | 50.0 | 57.1 | 50.0 | |||
| Amikacin | 98.2 | 87.5 | 100 | 75.0 | |||
| Colistin | NA | NA | NA | NA | |||
| Dominican Republic | (64) | (5) | (4)d | (2) | |||
| Ceftazidime-avibactam | 98.4 | 80.0 | 100 | 50.0 | |||
| Ceftazidime | 93.8 | 60.0 | 75.0 | 0 | |||
| Cefepime | 96.9 | 60.0 | 75.0 | 0 | |||
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 96.9 | 60.0 | 75.0 | 0 | |||
| Meropenem | 92.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Levofloxacin | 78.1 | 60.0 | 75.0 | 0 | |||
| Amikacin | 87.5 | 80.0 | 100 | 50.0 | |||
| Colistin | NA | NA | NA | NA | |||
| Guatemala | (149) | (42) | (26)e | (33) | |||
| Ceftazidime-avibactam | 90.6 | 66.7 | 100 | 57.6 | |||
| Ceftazidime | 75.8 | 38.1 | 57.7 | 18.2 | |||
| Cefepime | 73.8 | 23.8 | 38.5 | 0 | |||
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 71.8 | 21.4 | 34.6 | 0 | |||
| Meropenem | 71.8 | 0 | 0 | 6.1 | |||
| Levofloxacin | 70.5 | 16.7 | 23.1 | 3.0 | |||
| Amikacin | 79.2 | 33.3 | 50.0 | 15.2 | |||
| Colistin | NA | NA | NA | NA | |||
| Mexico | (562) | (238) | (29) | (160) | (167) | ||
| Ceftazidime-avibactam | 80.2 | 55.0 | 10.3 | 79.4 | 38.9 | ||
| Ceftazidime | 64.4 | 32.8 | 3.4 | 48.1 | 9.6 | ||
| Cefepime | 65.7 | 31.5 | 6.9 | 44.4 | 9.0 | ||
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 64.1 | 31.1 | 3.4 | 43.1 | 8.4 | ||
| Meropenem | 57.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.6 | ||
| Levofloxacin | 59.3 | 23.9 | 3.4 | 33.8 | 7.2 | ||
| Amikacin | 74.6 | 42.9 | 3.4 | 56.9 | 25.7 | ||
| Colistin | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | ||
| Panama | (80) | (21) | (13)f | (11) | |||
| Ceftazidime-avibactam | 87.5 | 52.4 | 84.6 | 36.4 | |||
| Ceftazidime | 82.5 | 38.1 | 61.5 | 18.2 | |||
| Cefepime | 82.5 | 38.1 | 61.5 | 9.1 | |||
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 77.5 | 28.6 | 46.2 | 9.1 | |||
| Meropenem | 73.8 | 0 | 0 | 9.1 | |||
| Levofloxacin | 63.7 | 23.8 | 38.5 | 9.1 | |||
| Amikacin | 88.8 | 57.1 | 92.3 | 45.5 | |||
| Colistin | NA | NA | NA | NA | |||
| Venezuela | (237) | (77) | (23)g | (62) | |||
| Ceftazidime-avibactam | 75.9 | 26.0 | 73.9 | 12.9 | |||
| Ceftazidime | 71.3 | 18.2 | 56.5 | 4.8 | |||
| Cefepime | 71.7 | 18.2 | 43.5 | 4.8 | |||
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 69.6 | 16.9 | 47.8 | 3.2 | |||
| Meropenem | 67.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Levofloxacin | 53.2 | 3.9 | 8.7 | 1.6 | |||
| Amikacin | 74.3 | 23.4 | 60.9 | 8.1 | |||
| Colistin | NA | NA | NA | NA | |||
Abbreviations: NS, non-susceptible; MBL-, no gene encoding a metallo-β-lactamase was detected by PCR; carbapenemase+/-, a gene encoding a serine carbapenemase was (+) or was not (-) detected by PCR; multidrug-resistant, isolates resistant to three or more sentinel agents from different drug classes; NA, no breakpoint available.
No acquired ESBLs or carbapenemases were detected in 58.8% (491/835) of meropenem-nonsusceptible P. aeruginosa isolates screened for genes encoding β-lactamases (Fig. 3), implying the role of chromosomally-coded mechanisms in meropenem resistance such as alterations in OprD or efflux pump expression, likely combined with hyper-production of the intrinsic chromosomal AmpC β-lactamase of P. aeruginosa. Among β-lactamase-positive isolates, VIM-type MBLs were the most common acquired β-lactamases identified, followed by KPC. VIM-positive isolates were identified in all countries surveyed except the Dominican Republic and accounted for 68.8% of meropenem-nonsusceptible isolates collected in Venezuela and 36.7-38.1% of meropenem-nonsusceptible isolates from Chile, Guatemala, and Panama. KPC, which is rarely found in P. aeruginosa collected outside of Latin America, was identified in isolates from Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Guatemala, and Mexico and was co-carried with VIM-type (n = 9) or IMP-type and GES-type carbapenemases (n = 2) in a small number of isolates. The majority (72.4%; 21/29) of P. aeruginosa carrying IMP-type MBLs and all isolates carrying GES-type carbapenemases were identified in Mexico, whereas SPM-positive isolates were only identified in Brazil. Carbapenemase-negative, ESBL-positive isolates were found primarily in Chile (10% of isolates, 12/120) and Mexico (13.9%, 33/238). Ceftazidime-avibactam was not active against isolates carrying MBLs (4.2% susceptible), as expected, and it also demonstrated reduced activity against MBL-negative, ESBL-positive isolates (34.0% susceptible) and GES carbapenemase-positive isolates (10.3%) (Table 6). These isolates may have carried additional β-lactamases that were not included in the molecular testing algorithm and that were not inhibited by avibactam, or may contain non-enzymatic resistance mechanisms. In contrast, 64.7% of KPC-positive isolates (MIC90, 32 µg/ml) and 92.5% of meropenem non-susceptible isolates in which no acquired β-lactamase was detected were susceptible to ceftazidime-avibactam (MIC90, 8 µg/ml).
β-lactamases identified in meropenem-nonsusceptible P. aeruginosa collected in 10 Latin American countries as part of the ATLAS global surveillance program from 2017 to 2019LA, Latin America; AR, Argentina; BR, Brazil; CL, Chile; CO, Colombia; CR, Costa Rica; DO, Dominican Republic; GT, Guatemala; MX, Mexico; PA, Panama; VE, Venezuela; Cpase, carbapenemase; ESBL, extended-spectrum β-lactamase; None detected, no gene encoding an acquired β-lactamase was detected by PCR. ESBL (cpase-) included isolates carrying ESBL-like GES-type and PER-type β-lactamases.
In vitro activity of ceftazidime-avibactam and comparator agents against β-lactamase-positive P. aeruginosa isolates collected in the Latin American region as part of the ATLAS global surveillance program from 2017 to 2019.
| Antimicrobial agent | MIC (µg/ml) | Interpretation (CLSI) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organism, phenotype/genotype (no. of isolates) | MIC50 | MIC90 | % Susceptible | % Intermediate | % Resistant | |
| ESBL-positive (50)a | Ceftazidime-avibactam | 32 | 128 | 34.0 | NA | 66.0 |
| Ceftazidime | >128 | >128 | 0 | 0 | 100 | |
| Cefepime | >16 | >16 | 0 | 4.0 | 96.0 | |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | >64 | >64 | 8.0 | 34.0 | 58.0 | |
| Meropenem | >8 | >8 | 0 | 16.0 | 84.0 | |
| Levofloxacin | >8 | >8 | 0 | 0 | 100 | |
| Amikacin | >32 | >32 | 14.0 | 4.0 | 82.0 | |
| Colistin | 1 | 2 | NA | 98.0 | 2.0 | |
| KPC-positive (51)b | Ceftazidime-avibactam | 8 | 32 | 64.7 | NA | 35.3 |
| Ceftazidime | 128 | >128 | 2.0 | 3.9 | 94.1 | |
| Cefepime | >16 | >16 | 0 | 0 | 100 | |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | >64 | >64 | 0 | 0 | 100 | |
| Meropenem | >8 | >8 | 0 | 0 | 100 | |
| Levofloxacin | >8 | >8 | 11.8 | 2.0 | 86.3 | |
| Amikacin | 16 | >32 | 52.9 | 13.7 | 33.3 | |
| Colistin | 1 | 1 | NA | 100 | 0 | |
| GES-type carbapenemase-positive (29)c | Ceftazidime-avibactam | 64 | 64 | 10.3 | NA | 89.7 |
| Ceftazidime | >128 | >128 | 3.4 | 3.4 | 93.1 | |
| Cefepime | >16 | >16 | 6.9 | 0 | 93.1 | |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | >64 | >64 | 3.4 | 6.9 | 89.7 | |
| Meropenem | >8 | >8 | 0 | 0 | 100 | |
| Levofloxacin | >8 | >8 | 3.4 | 0 | 96.6 | |
| Amikacin | >32 | >32 | 3.4 | 0 | 96.6 | |
| Colistin | 1 | 1 | NA | 100 | 0 | |
| MBL-positive (214)d | Ceftazidime-avibactam | 32 | >128 | 4.2 | NA | 95.8 |
| Ceftazidime | 64 | >128 | 1.4 | 6.5 | 92.1 | |
| Cefepime | >16 | >16 | 4.2 | 27.1 | 68.7 | |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 64 | >64 | 4.7 | 54.7 | 40.7 | |
| Meropenem | >8 | >8 | 0 | 2.3 | 97.7 | |
| Levofloxacin | >8 | >8 | 3.7 | 1.9 | 94.4 | |
| Amikacin | >32 | >32 | 14.0 | 8.4 | 77.6 | |
| Colistin | 1 | 2 | NA | 100 | 0 | |
| No acquired β-lactamase (479) | Ceftazidime-avibactam | 4 | 8 | 92.5 | NA | 7.5 |
| Ceftazidime | 8 | 64 | 59.9 | 8.1 | 31.9 | |
| Cefepime | 8 | >16 | 54.5 | 21.9 | 23.6 | |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 32 | >64 | 46.8 | 21.1 | 32.2 | |
| Meropenem | 8 | >8 | 0 | 28.2 | 71.8 | |
| Levofloxacin | 2 | >8 | 35.3 | 16.5 | 48.2 | |
| Amikacin | 4 | >32 | 77.2 | 3.8 | 19.0 | |
| Colistin | 1 | 2 | NA | 99.8 | 0.2 | |
ESBL-positive, isolates in which one or more β-lactamase genes encoding a PER-type or GES-type ESBL was detected by PCR; does not include isolates that co-carry serine carbapenemases or MBLs.
KPC-positive, isolates in which a gene encoding a KPC carbapenemase was detected by PCR; includes isolates that co-carry original (narrow) spectrum β-lactamases but does not include isolates that co-carry ESBLs or MBLs.
GES-type carbapenemase-positive, isolates in which a gene encoding GES-20 was detected by PCR; includes isolates that co-carry GES-type ESBLs (GES-1, GES-19, GES-26) but does not include isolates that co-carry other serine β-lactamases or MBLs.
MBL-positive, isolates in which a gene encoding an NDM-type, IMP-type, VIM-type or SPM-type MBL was detected by PCR; includes isolates that co-carry serine β-lactamases (original (narrow) spectrum β-lactamases, PER-type or GES-type ESBLs, KPC or GES-type carbapenemases) and five isolates co-carrying two MBLs (IMP-18 and VIM-2).
The current study summarizes the in vitro antimicrobial susceptibility and molecular β-lactamase carriage of isolates collected as part of the ATLAS global surveillance program from 2017 to 2019 in 10 Latin American countries. Earlier publications only included isolates from six of the 10 countries (Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Mexico, and Venezuela) described in the current study.2,3 In 2018, laboratory sites in Costa Rica, Dominican Republic, Guatemala, and Panama were added to the ATLAS global surveillance program and this is the first publication of data from those four countries as part of ATLAS or any other study.
In 2012-2015, 99.7% of Enterobacterales isolates (n = 7665) collected in Latin America as part of the ATLAS surveillance program were susceptible to ceftazidime-avibactam.3,24 In the 2015-2017 ATLAS report, 99.3% of Enterobacterales isolates (n = 7729) were susceptible to ceftazidime-avibactam.2 In the current study of 2017-2019 isolates, 98.1% of Enterobacterales were susceptible to ceftazidime-avibactam. The lower susceptibility to ceftazidime-avibactam observed in the current study is partly attributable to the inclusion of isolates from Guatemala, which displayed a >10% lower percentage of susceptibility than observed for isolates from all other countries (Table 2). Removal of isolates from Guatemala from the current dataset resulted in 98.7% (7946/8052) of Enterobacterales being susceptible to ceftazidime-avibactam (data not shown), a 1.0% decrease from 2012-2015. Further limiting the dataset to only isolates collected in Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Mexico, and Venezuela (i.e. the six countries included in the 2012–20153 and 2015–20172 study reports), 98.6% (7256/7358) of Enterobacterales collected in 2017-2019 were susceptible to ceftazidime-avibactam (data not shown), a 1.1% decrease from 2012 to 2015. The changes in susceptibility to ceftazidime-avibactam correlated with increases in the incidence of MBLs in Latin American isolates over time: 0.2% of isolates collected in 2012-2015 were MBL-positive3; 0.6% of isolates collected in 2015–20172; and 1.3% (95/7358; isolates from the six countries participating since 2012) or 1.7% (146/8416; isolates from all 10 countries) collected in 2017–2019 were MBL-positive (Fig. 2). The proportion of MBL-positive isolates collected in Guatemala in 2017-2019 (12.9% of isolates) was much higher than observed for the nine other countries surveyed (≤2.2%). Earlier data from Guatemala are not published and it is not possible to determine whether the abundance of MBL-positive Enterobacterales is due to recent or distant emergence.
In the current study, KPC was the most common carbapenemase identified, accounting for 61.5% of meropenem-nonsusceptible Enterobacterales from all 10 countries surveyed and 66.5% (339/510; data not shown) of isolates from the six countries included in the 2012–2015 and 2015–2017 ATLAS reports. In the 2012–2015 report, KPC carbapenemases comprised 89.1% of detected carbapenemases and MBLs were only identified in isolates from Colombia, Mexico, and Venezuela.3 In the current study, MBL-positive isolates were detected in eight of 10 countries surveyed and the proportion of carbapenemase-positive isolates that carried MBLs increased more than two-fold for isolates collected in Colombia and Venezuela compared to the 2012–2015 report.
Previous surveillance studies have reported phenotypic and genotypic ESBL rates in Latin American countries of 20->40% for both E. coli and K. pneumoniae, as well as rates of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales that often exceed 10%, particularly for K. pneumoniae and Enterobacter spp.2,3,21–23 In the current study, 6.0% of isolates were meropenem-resistant and genes encoding ESBLs were identified in 25.7% (2161/8416) of collected Enterobacterales isolates. The distribution of ESBL and carbapenemase types observed in the current study was in general agreement with previous reports for South American countries and Mexico2,3,29 and the ESBL rate compared well to that reported for isolates tested in 2015–2017 (24.1%), when similar molecular testing criteria were applied.2 In the current study, we found that ceftazidime-avibactam continues to inhibit ESBL-positive, AmpC-positive, ESBL- and AmpC-positive, GES-type carbapenemase-positive, and OXA-48-like-positive isolates of Enterobacterales (≥99.8% susceptible), as was found in earlier studies.2,3
The current study identified 156 isolates of Enterobacterales (1.9% of all isolates) that were resistant to ceftazidime-avibactam (Table 1); 144 (92.3%) of these 156 isolates were MBL-positive (Table 3). The mechanism(s) of reduced susceptibility for the remaining 12 isolates may reflect the presence of an avibactam-insensitive β-lactamase that was not detected using the current molecular algorithm17,18 or a combination of mechanisms, such as increased β-lactamase production with porin deficiency and altered efflux and/or penicillin-binding protein alterations.6–13,30,31 It should be noted that four of these isolates carried PER-2 or PER-4 β-lactamases that are inhibited less effectively by avibactam in some cases.13,15
In the current study, 86.9% of all isolates of P. aeruginosa tested from 10 Latin American countries were susceptible to ceftazidime-avibactam (Table 4), similar to the ATLAS study reports for isolates collected in 2012–2015 (87.4% susceptible)3 and 2015–2017 (86.6% susceptible).2 Other studies reported 84.0% (21/25) of P. aeruginosa collected in 2014-2015 to be susceptible to ceftazidime-avibactam19 and a ceftazidime-avibactam MIC90 of 16 µg/ml for 13 isolates of P. aeruginosa tested in 2011.20 Among clinical isolates of P. aeruginosa from Latin American countries, other investigators have reported country-specific percentages of susceptibility to ceftazidime that ranged from 50-80%, while 60-70% of isolates were carbapenem-susceptible,2,3,23 similar to the findings in the current study.
In the current study, 25.6% of all meropenem-nonsusceptible P. aeruginosa isolates collected in Latin America and 24.8% of isolates from the six countries participating in the study since 2012 carried MBLs. In comparison, 110 MBL-positive P. aeruginosa isolates were identified among 750 isolates nonsusceptible to meropenem, doripenem or imipenem in the 2012–2015 ATLAS report.3 VIM-type enzymes continue to predominate among carbapenemase-positive isolates in the region, comprising 60.5% of carbapenemase-positive P. aeruginosa from all 10 countries and 63.3% of carbapenemase-positive P. aeruginosa from the six countries participating since 2012, compared to ∼50% of carbapenemase-positive isolates reported in the 2012–2015 report.3
We conclude that clinical isolates of Enterobacterales collected from 10 Latin America countries in 2017–2019, including MBL-negative meropenem-nonsusceptible isolates and isolates with an MDR phenotype, were highly susceptible to ceftazidime-avibactam, which was comparably active or more active in vitro than currently available agents of last resort (e.g., amikacin, colistin, tigecycline) that are associated with well-established toxicities. Similarly, ceftazidime-avibactam was the most potent agent tested against isolates of P. aeruginosa collected in these same countries in 2017–2019. Ceftazidime-avibactam has retained its in vitro potency against clinical isolates of Enterobacterales and P. aeruginosa collected from hospitalized patients in Latin American countries since 2012. Regional and country prevalence of different carbapenem-resistance mechanisms do exist and must be considered when evaluating treatment options.
FundingFunding for this research, which was performed at IHMA and included compensation for services related to preparing this manuscript, was provided by Pfizer, Inc. The sponsor participated in the development of the overall study design, but collection and testing of isolates, data analysis and manuscript preparation were independently performed by IHMA.
The authors gratefully acknowledge and thank all ATLAS global surveillance program participants and IHMA laboratory personnel for their contributions to the ATLAS global surveillance program.












![β-lactamases identified in meropenem-nonsusceptible Enterobacterales isolates collected in ten Latin American countries as part of the ATLAS global surveillance program from 2017 to 2019LA, Latin America; AR, Argentina; BR, Brazil; CL, Chile; CO, Colombia; CR, Costa Rica; GT, Guatemala; MX, Mexico; PA, Panama; VE, Venezuela; Cpase, carbapenemase; ESBL, extended-spectrum β-lactamase; None detected, no gene encoding an acquired β-lactamase was detected by PCR. ESBL (cpase-) included isolates carrying CTX-M-type [CTX-M-15 (n = 28), CTX-M-2 (n = 8), CTX-M-15 and CTX-M-2 or TEM-type ESBL (n = 7), CTX-M-1 group (n = 7), CTX-M-8 (n = 1)] and SHV-type (n = 1) ESBLs that were assumed to harbor permeability defects. One meropenem-nonsusceptible (MEM-NS) isolate collected in Guatemala was not molecularly characterized for β-lactamase genes. No MEM-NS Enterobacterales isolates were collected in the Dominican Republic during the surveyed time period. β-lactamases identified in meropenem-nonsusceptible Enterobacterales isolates collected in ten Latin American countries as part of the ATLAS global surveillance program from 2017 to 2019LA, Latin America; AR, Argentina; BR, Brazil; CL, Chile; CO, Colombia; CR, Costa Rica; GT, Guatemala; MX, Mexico; PA, Panama; VE, Venezuela; Cpase, carbapenemase; ESBL, extended-spectrum β-lactamase; None detected, no gene encoding an acquired β-lactamase was detected by PCR. ESBL (cpase-) included isolates carrying CTX-M-type [CTX-M-15 (n = 28), CTX-M-2 (n = 8), CTX-M-15 and CTX-M-2 or TEM-type ESBL (n = 7), CTX-M-1 group (n = 7), CTX-M-8 (n = 1)] and SHV-type (n = 1) ESBLs that were assumed to harbor permeability defects. One meropenem-nonsusceptible (MEM-NS) isolate collected in Guatemala was not molecularly characterized for β-lactamase genes. No MEM-NS Enterobacterales isolates were collected in the Dominican Republic during the surveyed time period.](https://static.elsevier.es/multimedia/14138670/0000002500000006/v1_202112201713/S1413867021001161/v1_202112201713/en/main.assets/thumbnail/gr2.jpeg?xkr=ue/ImdikoIMrsJoerZ+w95uaF0+42b+pWE4hY44gaZY=)