A 38-year-old woman was referred to the department of Oral Pathology at the Universidade Paulista, Goiânia, Brazil, complaining of multiple painful ulcers on the gum and upper lip mucosa. The patient was six month pregnant and had regularly attended prenatal visits. The patient had a history of weight loss due to inability to swallow solid foods in the last two months. Also, the patient complained of drooling. Her pulse and blood pressure were normal.
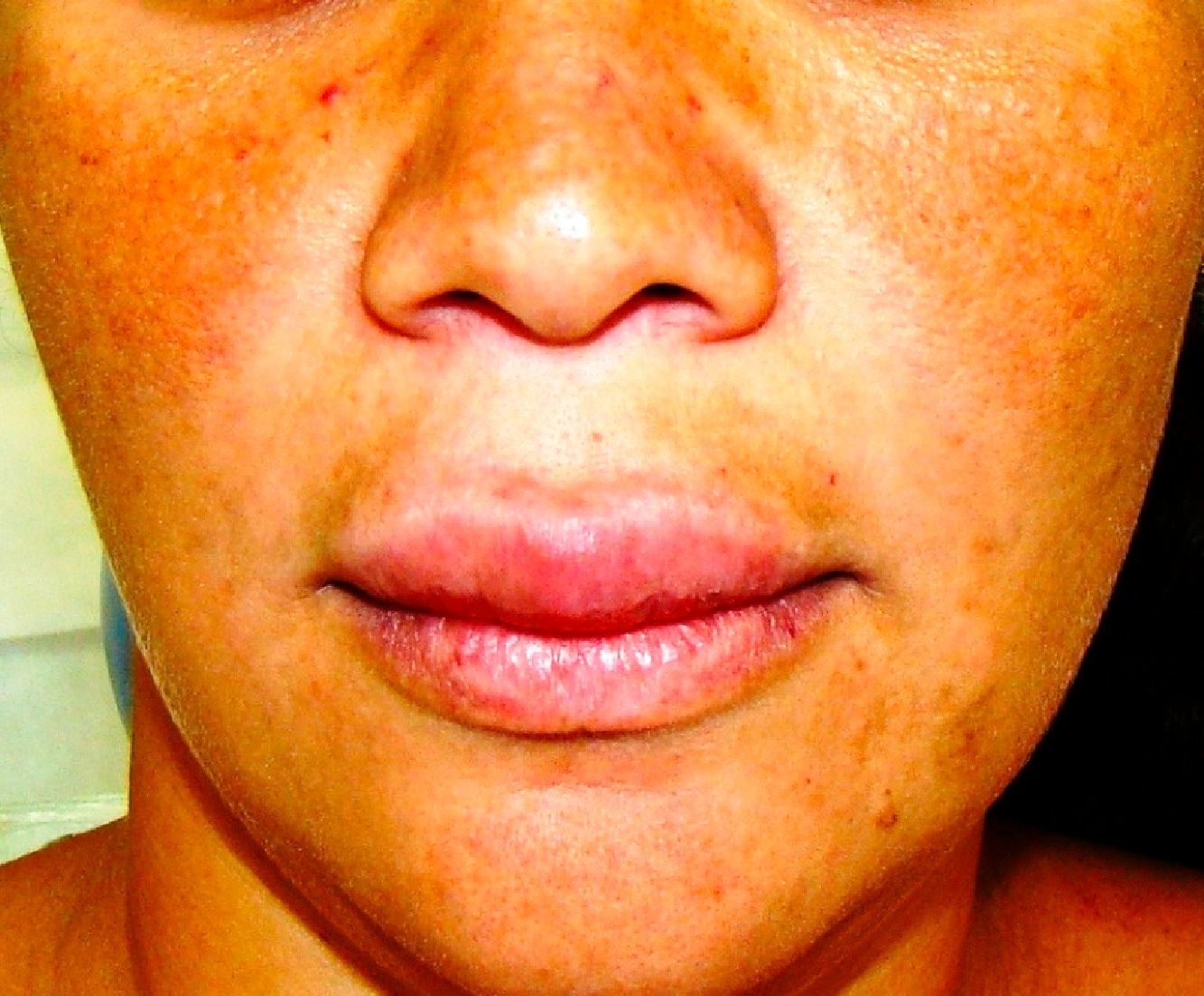
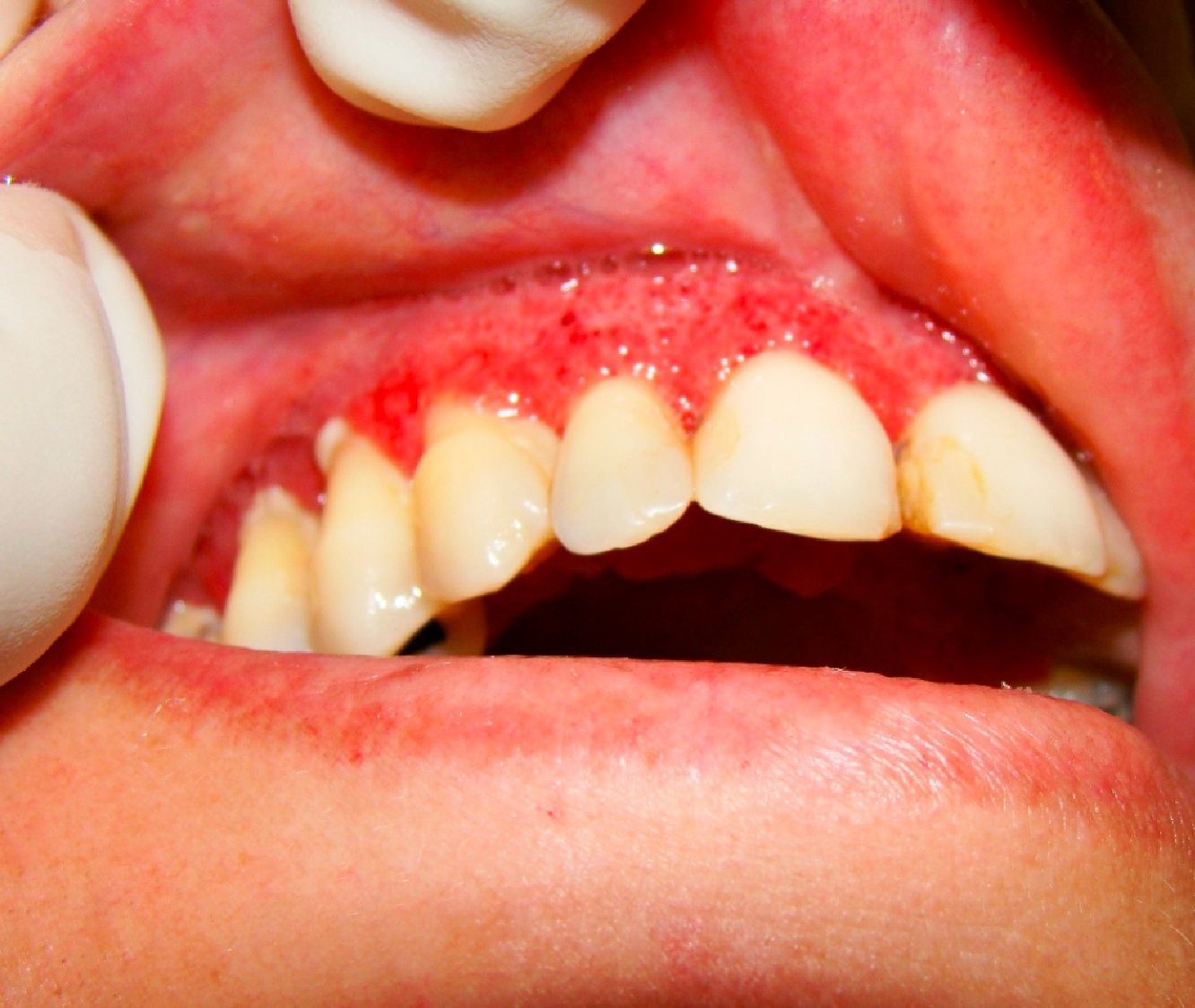
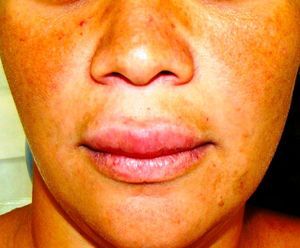
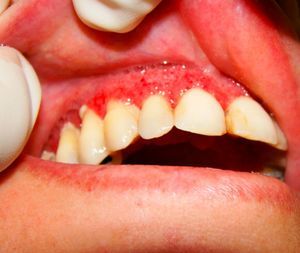
Clinical examination revealed palpable lymph nodes in the submandibular region. The facial muscles were normal and showed no visible asymmetry. The intra oral examination showed the presence of multiple painful moriform ulcers in the upper gum, palate and upper lip. The lesion on her lip was similar to a granulomatous cheilitis (Fig. 1). The gum lesions were mulberry-like, with distinctly visible hemorrhagic pinpoints on the surface (Fig. 2). The teeth involved had severe degrees of mobility, such as in periodontal disease.
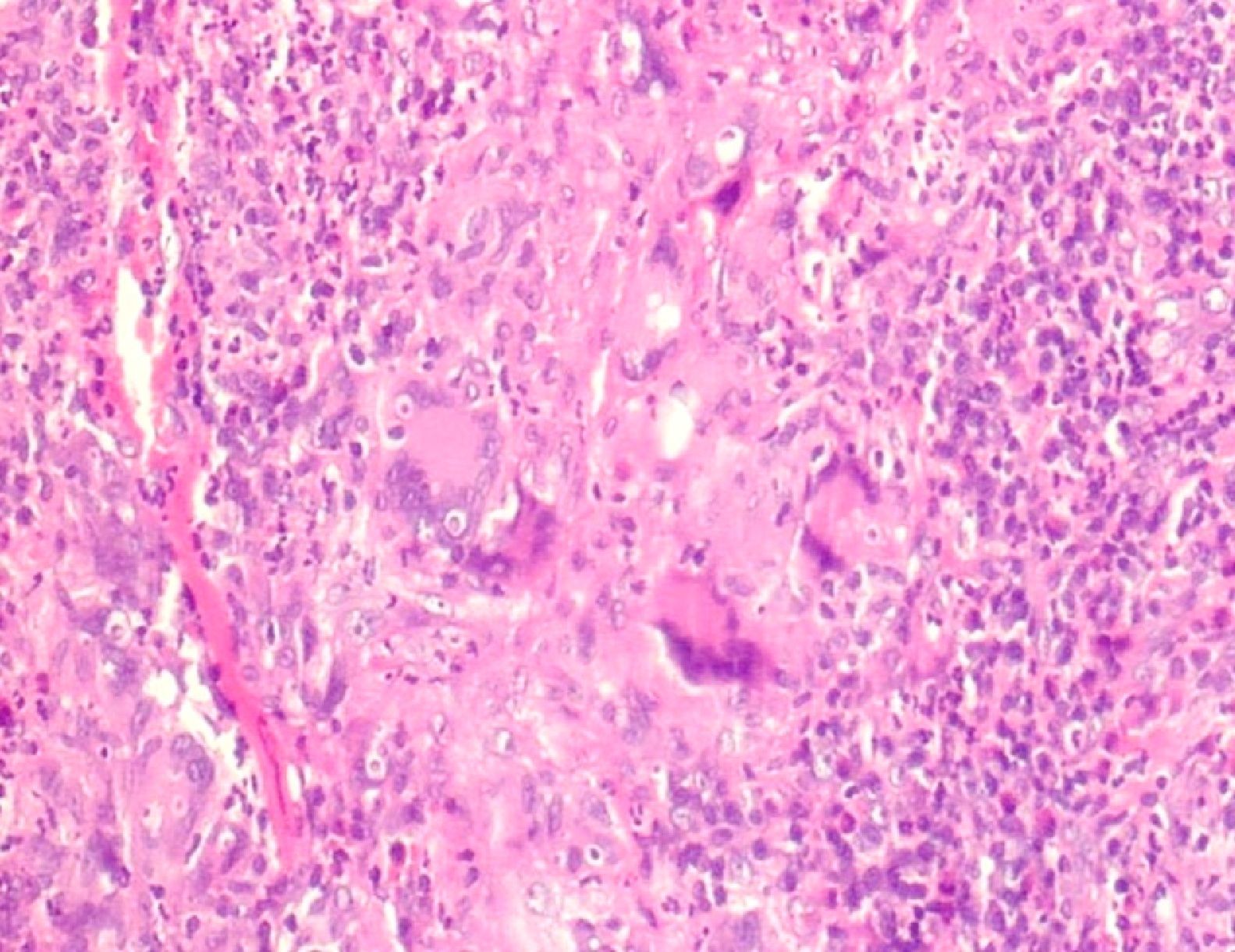
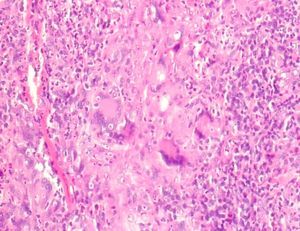
Incisional biopsy was performed in the gum, where the histological sections revealed the presence of granulomatous inflammation, with pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia, with the presence of macrophages, epithelioid cells, multinucleated giant cells, histiocytes, as well as lymphocytes (Fig. 3). Analysis with periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining revealed the presence of typical yeast, thus confirming the diagnosis of paracoccidioidomycosis (PM).
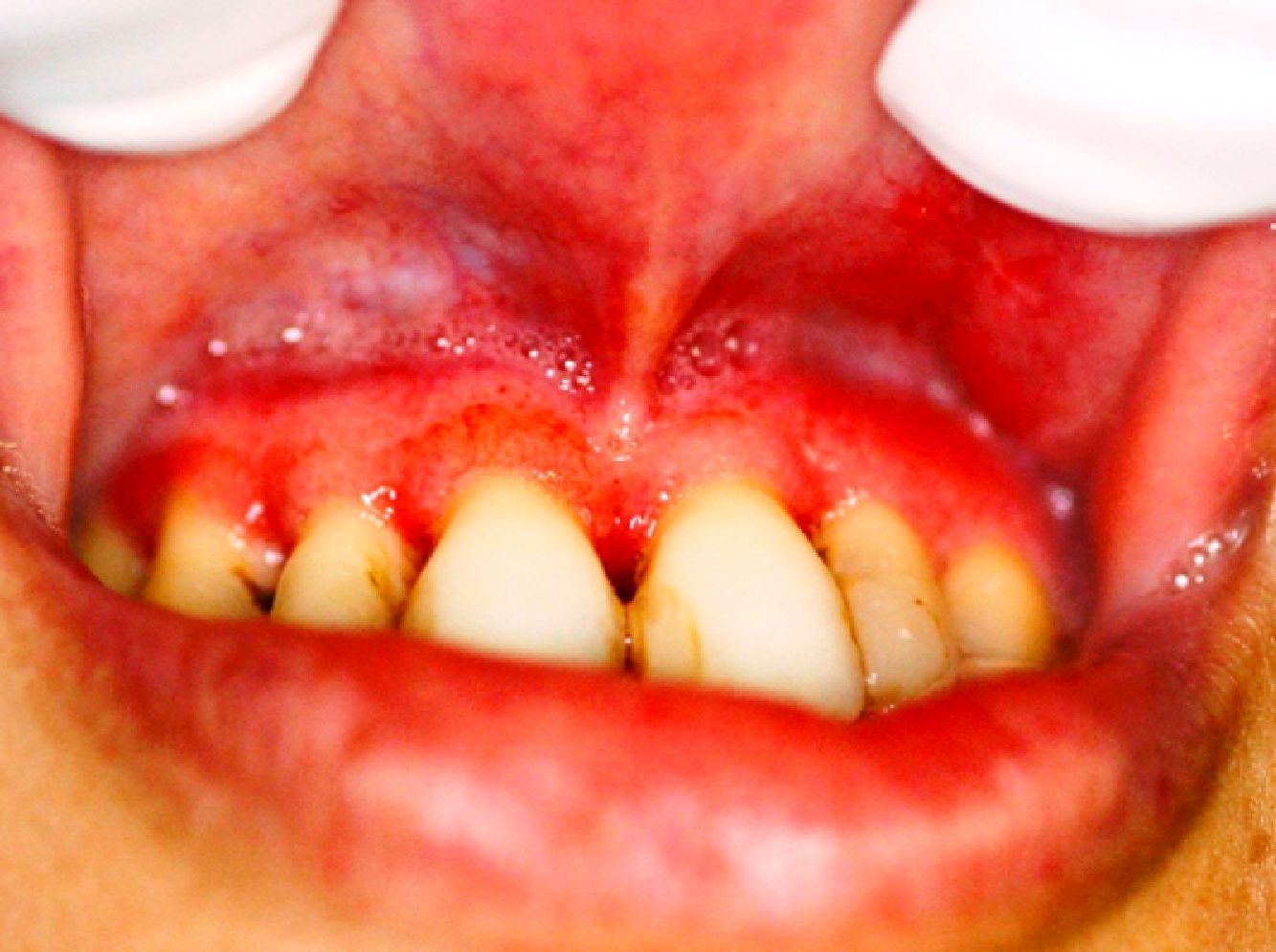
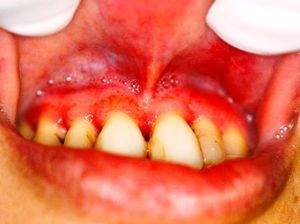
The patient was referred to the University Hospital in Goiania. After examination and confirmation of pulmonary involvement by radiographic exams, she was treated with intravenous amphotericin B for one month (Fig. 4). Thereafter, the patient received oral treatment, leading to a reduction of the clinical lesions. Before the end of treatment, the baby was delivered prematurely at eight months of gestation; twenty days after delivery, the mother died.
Epidemiologic studies show that in adults, males are more commonly affected than females, at a ratio of 10:1. The higher incidence and gravity in males than in females has been attributed to the natural protector effect of female hormones (estrogen) against the fungus, influencing its pathogenesis in humans by inhibiting the transition of conidia or mycelia to yeast, the pathogenic form of this organism.1–3 When PM affects women, it usually occurs before menarche or after menopause, being particularly uncommon in women of childbearing age, especially in pregnant women.2,4 It is known that the immunological changes characteristic of pregnancy can exacerbate the natural history of systemic fungal infections; however, that is well accepted when associated with HIV infection.3,4 Herein, the patient was in the sixth month of pregnancy and showed no immunological changes. These facts make the diagnosis of the systemic fungal infection unexpected.
Conflict of interestAll authors declare to have no conflict of interest.