The antigenic potential of seven immunogenic peptides of the dengue virus was evaluated in the sera of patients with dengue confirmed by IgM/IgG serology. Antibodies IgM and IgG against dengue virus peptides were analyzed by ELISA in 31 dengue sero-positive and 20 sero-negative patients. The P5 peptide showed significant IgG immunoreactivity mostly in the sera of patients with dengue without warning signs in comparison with patients with dengue with warning signs, correlating with mild disease. This finding suggests that the low antibody response against P5 epitope could be a risk factor for higher susceptibility to dengue virus infection with warning signs, and that P5 could be a potential antigen for vaccine development.
Identification of the B- and T-cell epitopes of dengue virus (DENV) with antigenic potential has been important in understanding the pathogenesis of dengue and to develop vaccines. Thus, it was observed that T-cell responses to the original infecting serotype might limit responses directed against epitopes that are either cross-reactive or specific for a secondary infecting serotype.1 In addition, the low magnitude of HLA restricted responses of CD8+ by predicted epitopes correlated with disease susceptibility, whereas higher-magnitude responses were associated with more polyfunctional and protective CD8+ T cells.2 A high throughput study of T-cell responses to DENV-2 peptides revealed a significant association between the magnitude of T-cell activation, mostly by NS3 protein and dengue severity.3 On the other hand, monoclonal antibodies against epitopes of NS1 cross-react with molecules expressed by platelets or with endothelial cells, which can be associated with plasma leakage in severe dengue.4–6
We reported several B- and T-cell DENV epitopes identified by an immunoinformatic strategy, seven highly immunogenic peptides induced mostly antibodies (P5, P13, and P19) and/or CD4+ T cells (P15, P18, P20, and P22) in mice.7 Four of these peptides belong to the protein NS5 (P18, P19, P20, and P22), whereas P15, P13, and P5 are included in the amino-acid sequences of NS4b, NS4a, and E proteins, respectively. Here, we analyzed the antigenicity of these peptides by the detection of anti-DENV antibodies in the sera of patients with dengue.
We aimed to identify the epitopes in DENV useful for evaluation of humoral immune response against the four serotypes related with mild and severe clinical manifestations, and their implications for vaccine development.
Serum samples were obtained from patients with a clinical and laboratory diagnosis of dengue at the Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social in Yucatán, Mexico. Ethical approval was obtained from the Ethics Committee of the Institution (Approval Code No. 2010-785-041). As surveillance is mandatory at the Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social, there is no requirement for informed consent, but all data were maintained in privacy. All samples were tested by a Dengue IgG/IgM Lafon® immunochromatographic cassette (Standard Diagnostics, Inc., Korea), with Dengue IgM Capture ELISA (E-DEN01M/E-DEN01M05) and Dengue IgG Capture ELISA (E-DEN02G PanBio®, Brisbane, Australia). Sero-positive patients were further classified into dengue without warning signs (DWOWS) or dengue with warning signs (DWWS) groups according to the World Health Organization (WHO) classification.8 To compare the results employing the 1997 WHO Dengue Case Classification,9 the sero-positive patients were also grouped into dengue fever (DF) or dengue hemorrhagic fever (DHF).
The immunoreactivities of the reported synthetic peptides P5, P13, P19, P15, P18, P20, and P22 were analyzed by ELISA to detect IgM and IgG antibodies in the sera of patients with dengue as reported.7 All tests were run in triplicate.
Statistical significance was established at p<0.05 for all parameters. Median values of optical density (OD) 490nm between groups were compared by the non-parametric Mann–Whitney U test utilizing SPSS version 18 statistical software. Estimation of risk or protection factor was determined by odds ratio (OR).
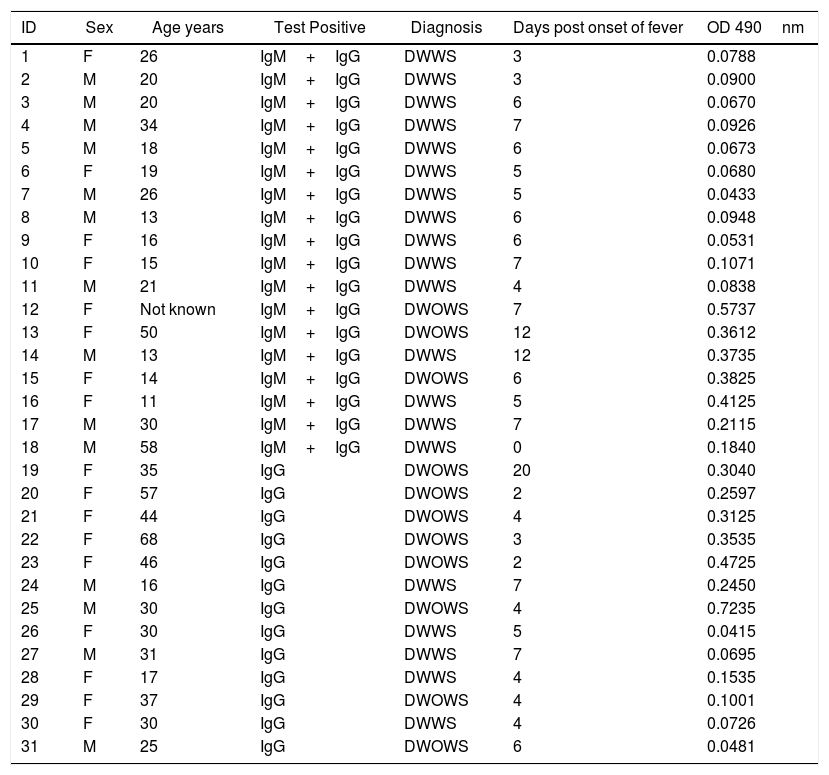
Thirty-one serum samples were confirmed with DENV infection from 14 male and 17 female patients, age between 11 and 68 years with an average of 28.61 years. Thirteen patients were only IgG-positive and 18 were IgG+IgM-positive (Table 1). There were 10 patients confirmed with mild disease (DWOWS), and 21 had severe dengue (DWWS).
Diagnosis and serologic characteristics of DENV infection in the population studied.
| ID | Sex | Age years | Test Positive | Diagnosis | Days post onset of fever | OD 490nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F | 26 | IgM+IgG | DWWS | 3 | 0.0788 |
| 2 | M | 20 | IgM+IgG | DWWS | 3 | 0.0900 |
| 3 | M | 20 | IgM+IgG | DWWS | 6 | 0.0670 |
| 4 | M | 34 | IgM+IgG | DWWS | 7 | 0.0926 |
| 5 | M | 18 | IgM+IgG | DWWS | 6 | 0.0673 |
| 6 | F | 19 | IgM+IgG | DWWS | 5 | 0.0680 |
| 7 | M | 26 | IgM+IgG | DWWS | 5 | 0.0433 |
| 8 | M | 13 | IgM+IgG | DWWS | 6 | 0.0948 |
| 9 | F | 16 | IgM+IgG | DWWS | 6 | 0.0531 |
| 10 | F | 15 | IgM+IgG | DWWS | 7 | 0.1071 |
| 11 | M | 21 | IgM+IgG | DWWS | 4 | 0.0838 |
| 12 | F | Not known | IgM+IgG | DWOWS | 7 | 0.5737 |
| 13 | F | 50 | IgM+IgG | DWOWS | 12 | 0.3612 |
| 14 | M | 13 | IgM+IgG | DWWS | 12 | 0.3735 |
| 15 | F | 14 | IgM+IgG | DWOWS | 6 | 0.3825 |
| 16 | F | 11 | IgM+IgG | DWWS | 5 | 0.4125 |
| 17 | M | 30 | IgM+IgG | DWWS | 7 | 0.2115 |
| 18 | M | 58 | IgM+IgG | DWWS | 0 | 0.1840 |
| 19 | F | 35 | IgG | DWOWS | 20 | 0.3040 |
| 20 | F | 57 | IgG | DWOWS | 2 | 0.2597 |
| 21 | F | 44 | IgG | DWOWS | 4 | 0.3125 |
| 22 | F | 68 | IgG | DWOWS | 3 | 0.3535 |
| 23 | F | 46 | IgG | DWOWS | 2 | 0.4725 |
| 24 | M | 16 | IgG | DWWS | 7 | 0.2450 |
| 25 | M | 30 | IgG | DWOWS | 4 | 0.7235 |
| 26 | F | 30 | IgG | DWWS | 5 | 0.0415 |
| 27 | M | 31 | IgG | DWWS | 7 | 0.0695 |
| 28 | F | 17 | IgG | DWWS | 4 | 0.1535 |
| 29 | F | 37 | IgG | DWOWS | 4 | 0.1001 |
| 30 | F | 30 | IgG | DWWS | 4 | 0.0726 |
| 31 | M | 25 | IgG | DWOWS | 6 | 0.0481 |
DWWS, dengue with warning signs; DWOWS, dengue without warning signs. Cut off value 0.3486.
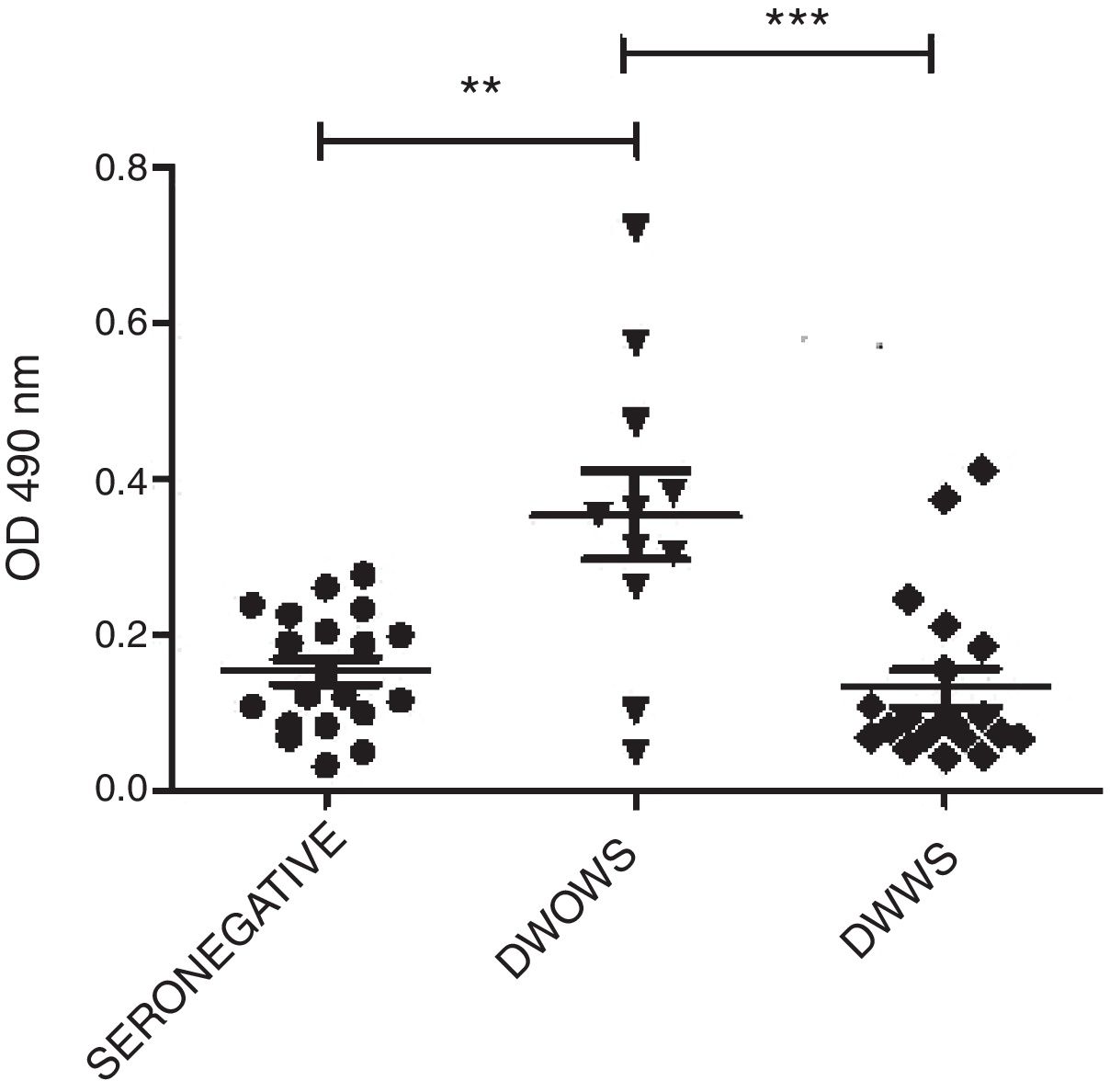
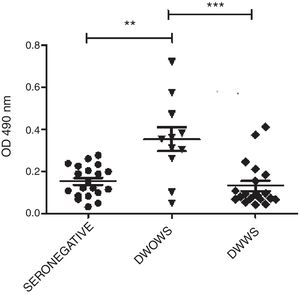
None of the seven P5, P13, P19 P15, P18, P20, and P22 peptides detected IgM antibodies in seropositive samples (data not shown). Very low OD 490nm levels were observed by ELISA IgG utilizing P13, P19, P15, P18, P20, and P22. Only P5 peptide detected variable levels of IgG antibodies in sera from 11 seropositive-patients with DWOWS (OD average, 0.354) and 20 patients with DWWS (OD average, 0.130). A statistically significant difference of median OD 490nm values of IgG was observed between these groups (Mann–Whitney U test, p=0.002) (Fig. 1). Median OD values among 16 patients under 25 years of age and 15 patients over 25 years was not significantly different (Mann–Whitney U test, p=0.252).
IgG antibodies detected with P5 in patients with dengue without warning signs (DWOWS) and dengue with warning signs (DWWS). Levels of IgG antibodies were detected by ELISA with P5 peptide in the sera of patients with DWOWS and in the sera of patients with DWWS. Mann–Whitney U test showed a statistically significant difference between the mean values of OD 490nm of the groups: sero-negative and DWOWS (p=0.004), DWOWS and DWWS (p=0.002).
The strong association between mild dengue and immunoreactivity of IgG antibodies against P5 was confirmed by means of OR=0.09 (range, 0.01–0.608). Similar results were obtained when seropositive patients were grouped according to the 1997 WHO Guidelines (data not shown).
Key differences in the immunodominance of DENV proteins for modulation of the adaptative immune response have been reported. In a previous study, we reported synthetic peptides from DENV epitopes that induced different immune responses in immunized mice.7
The P18, P19, P20, and P22 epitopes of the NS5 protein activated T CD4+ and B cells in mice, but they were unable to show similar activation in humans, as can be inferred from our negative IgG and IgM immunoreactivity results in the sera of patients with dengue. In contrast, Rivino et al. demonstrated that CD8+ cells preferentially target NS3 and NS5 epitopes, whereas CD4+ and B lymphocytes recognize E, C, and NS1 epitopes.10 The immunogenic peptide P57 is located in domain III of protein E, which has been implicated as a receptor binding domain, and several neutralizing monoclonal antibodies have their epitopes in this domain.11,12 In mice, P5 induced moderate antibody levels and more T CD8+ cell response, suggesting a lesser capacity for B-cell induction.7 However, different levels of IgG antibodies were detected in the serum samples of seropositive patients with dengue employing the P5 peptide in ELISA tests. As the P5 peptide is 89% conserve among the four DENV serotypes, it would be expected that the P5 peptide would be able to react similarly with antibodies from patients infected with different DENV. However, the P5 peptide has a single amino-acid variation in position 4 (R/K) in DENV-2 and DENV-4, which could be the reason for non-reactivity in some patients.
All patients but three with DWWS showed high levels of antibodies detected more than three days after the onset of fever, suggesting that P5 could detect antibodies during the early convalescent phase of secondary dengue infections. Furthermore, patients with the mild form of the disease had higher levels of IgG antibodies up to four and even seven days post-onset of fever, compared to patients with DWWS, according to both WHO classification systems.8,9
In addition, a strong association between high levels of anti-P5 antibodies and mild disease presentation was observed (OR=0.09), suggesting that, in secondary infections, low antibody response against P5 peptide could play a role in higher susceptibility for developing warning signs. Therefore, this could be relevant for the development of a potential vaccine. In this sense, we demonstrated the antigenicity of the P5 peptide, in addition to its immunogenicity in mice, increase its potential as a vaccine candidate against DENV infection.
In conclusion, a new antigenic epitope from the E protein of DENV previously identified in silico was able to detect IgG antibodies in the sera of humans with mild DENV infection, showing its potential use for studies on dengue pathogenesis, disease diagnosis and vaccine development.
FundingThe present study was supported by Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (grant number SALUD-2007-01-68909).
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Present address: Universidad Autónoma de Yucatán, Facultad de Medicina, Unidad Interinstitucional de Investigación Clínica y Epidemiología, Mérida, Mexico.
Present address: Tulane University, School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, Department of Tropical Medicine, New Orleans, USA.