The zoonotic potential to cause human and/or animal infections among multidrug-resistant extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli from avian origin was investigated. Twenty-seven extraintestinal pathogenic E. coli isolates containing the increased survival gene (iss) were obtained from the livers of healthy and diseased poultry carcasses at two slaughterhouses in Salvador, northeastern Brazil. The antimicrobial resistance-susceptibility profiles were conducted with antibiotics of avian and/or human use by the standardized disc-diffusion method. Antimicrobial resistance was higher for levofloxacin (51.8%), amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (70.4%), ampicillin (81.5%), cefalotin (88.8%), tetracycline (100%) and streptomycin (100%). The minimum inhibitory concentrations above the resistance breakpoints of doxycycline, neomycin, oxytetracycline and enrofloxacin reached, respectively, 88.0%, 100%, 75% and 91.7% of the isolates. Strains with high and low antimicrobial resistance were i.p. administered to Swiss mice, and histopathological examination was carried out seven days after infection. Resistance to goat and human serum complement was also evaluated. The results show that Swiss mice challenged with strain 2B (resistant to 11 antimicrobials) provoked a severe degeneration of hepatocytes besides lymphocytic infiltration in the liver, whereas the spleen showed areas of degeneration of the white and red pulp. Conversely, the spleen and liver of mice challenged with strain 4A (resistant to two antimicrobials) were morphologically preserved. In addition, complement resistance to goat and human serum was high for strain 2B and low for strain 4A. Our data show that multidrug resistance and pathogenesis can be correlated in extraintestinal pathogenic E. coli strains obtained from apparently healthy poultry carcasses, increasing the risk for human public healthy.
The spread of multidrug resistance among avian Escherichia coli is usually attributed to the selective pressure exerted by the antimicrobials included in broiler feed for the past 60 years.1 Johnson et al.2 reinforced this suspicion since antibiotic-resistant and antibiotic-susceptible E. coli isolates from retail poultry products had similar phylogenetic background, and otherwise emerged from the same source population. Regarding antimicrobial exposure in poultry production, multidrug resistance among extraintestinal pathogenic E. coli (ExPEC) allied to community acquired infections is increasing in prevalence in many parts of the globe.3 The indiscriminate use of antimicrobials is high in developing countries, where human antibiotics are often accessible for non-therapeutic uses in healthy animals.4 Therefore, colonization of asymptomatic poultry by multidrug resistant ExPEC augments the probability of resistance gene acquisition by human strains through the food-chain.
Avian pathogenic E. coli (APEC) is commonly reported as an ExPEC pathotype, but its genotype is not clearly defined. According to Kwon et al.5 at least five virulence genes are present in APEC, many of them found in plasmid pTJ100.6 However, the increased survival gene (iss) has been identified as a virulence marker to distinguish between avian and human ExPEC.7 This gene exerts anti-complement resistance and has been found in conserved regions of ColV and ColBM plasmids,8,9 which are often identified in APEc strains.6,10 Recent findings also suggest that APEC and human neonatal meningitis E. coli (NMEC) are subpathotypes from ExPEC involved in pathogenesis of both avian and human infections.11 Therefore, hybrid plasmids (ColV- and ColBM-associated plasmids) harboring a number of distinct virulence genes and MDR-encoding islands can also be present in ExPEC isolates.11 Consequently, it is now clear that selected high-virulent and multidrug resistant ExPEC strains of avian origin represent subpathotypes of great danger to human public health.
Brazil has ranked first in the world in exports of poultry meat since 2004.12 Typical selections of poultry in Brazilian slaughterhouses take into account macroscopic alterations that can result in discarding carcasses.13 However, sub-clinical symptoms are not always perceived and often do not show a clue of the presence of pathogenic microorganisms. Thus, the risk of virulence and drug resistance gene transmission between avian E. coli obtained trough the food-chain and intestinal commensal E. coli is increasing. The goal of the present study was to investigate the pathogenesis to mammalian hosts of selected multidrug resistant ExPEC strains obtained from healthy poultry carcasses in Salvador, Brazil.
Material and methodsExPEC strainsExtraintestinal pathogenic E. coli strains were obtained from the livers of poultry carcasses with (n=9) or without (n=18) macroscopic alterations at two slaughterhouses in Salvador, capital of the state of Bahia, northeast Brazil (Table 1). Carcasses without macroscopic alterations were considered healthy and approved for human consumption. The organs were collected under sterile conditions. All bacterial strains were identified through biochemical tests, and the presence of the iss gene was determined according to the method reported in a previous study.14 The isolates were maintained in tubes containing brain heart infusion agar at 8°C until use.
ExPEC strains obtained from the liver of poultry carcasses.
| E. coli | Macroscopic aspect | Presence of gene issa | Presence of gene stxb |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4A | No alteration | + | − |
| 5A | No alteration | + | − |
| 36A | No alteration | + | − |
| 41A | No alteration | + | − |
| 43A | No alteration | + | + |
| 44A | No alteration | + | − |
| 2B | No alteration | + | − |
| 5B | No alteration | + | − |
| 37B | No alteration | + | − |
| 38B | No alteration | + | + |
| 39B | No alteration | + | − |
| 42B | No alteration | + | − |
| 15C | No alteration | + | − |
| 21C | No alteration | + | − |
| 42C | No alteration | + | − |
| 32 | No alteration | + | − |
| 35 | No alteration | + | − |
| 46 | No alteration | + | + |
| 24A | Salmonella septicemia | + | − |
| 30C | Salmonella septicemia | + | − |
| 31C | Salmonella septicemia | + | − |
| 48A | Ascitis | + | − |
| 48B | Ascitis | + | − |
| 52B | Cachexy | + | − |
| 54B | Cachexy | + | − |
| 60A | Colibacillosis | + | − |
| 55B | Colibacillosis | + | − |
The resistance-susceptibility profiles to antimicrobials of avian or human use were determined by the standard disc-diffusion method, following the recommendations of the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (formally, National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards).15 Briefly, filter paper discs 5mm in diameter impregnated with antibiotics (Cecon) were added to cultures in Petri dishes (0,5 on the McFarland scale, corresponding to 108cells/mL) containing Mueller–Hinton agar (Oxoid). After 24h incubation at 35°C, the diameter of the inhibition zone was measured with a caliper. All tests were carried out in duplicate against 13 antimicrobials and the results were interpreted as sensitive, moderately sensitive or resistant. The breakpoints for resistance were those recommended by the CLSI. The overall resistance rate was calculated as the number of non-susceptible isolates divided by the total number of isolates. Multidrug resistance was determined when bacterial isolates were resistant to four antimicrobials of at least three different classes. The isolates obtained from a single sample with an identical antibiotic resistance/sensitivity profile were treated as a single strain. In this case, bacterial replicates were not conducted.
Minimum inhibitory concentration of typical antimicrobials used on Brazilian farmsThe minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antimicrobials commonly used on Brazilian farms (doxycycline, neomycin, oxytetracycline and enrofloxacin) was measured through the broth dilution method in concentrations ranging from 1,9 to 1000μg/mL.16 The MIC was the lowest concentration that caused visible inhibition of growth, while the minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) was the lowest concentration resulting in no growth after the incubation period of 24h at 37°C. All assays were performed in duplicate with 25 ExPEC strains resistant to 4–11 antimicrobials through the disc-diffusion method. A list of antimicrobials authorized by the Brazilian government to be included in broiler feed is shown in Table 2.
Antimicrobials authorized by Brazilian authorities used as growth promoters in broiler feed.
| Antimicrobial class | Antimicrobials | Dosage (g/ton) |
|---|---|---|
| Oligosaccharide | Avilamicin | 2,5–10 |
| Peptide | Bacitracin methylene disalicylate | 4–55 |
| Peptide | Zinc bacitracin | 4–55 |
| Benzene derivative | Chlorhexidine | 10–20 |
| Macrolide | Spiramycin | 5 |
| Peptide | Enramycin | 3–10 |
| Phosphoglycolipids | Flavomycin | 1–2 |
| Lincosamide | Lincomycin | 2,2–4,4 |
| Peptide | Colistin sulfate | 2–10 |
| Streptogramin | Virginiamycin | 5,5–16.5 |
| Quinolone | Clorohidroxiquinolin | 15–30 |
| Macrolide | Tylosin tartrate/phosphate | 4–55 |
The complement resistance test was carried out with selected ExPEC strains obtained from healthy carcasses, and with distinct drug resistance profile, following the method adapted from Samuelsen et al.17 Samples of blood were obtained from goats and a healthy human volunteer under sterile conditions and allowed to coagulate. The blood was centrifuged (7000rpm/5min) and blood serum was separated into a new tube. Briefly, 190μL of the serum plus 10μL of E. coli strains (107cells/mL) were cultured together in wells of sterile Elisa plates, and incubated at 37°C for 180min. Then, aliquots of 10μL were sampled at times 0, 60, 120 and 180min, and added to Petri dishes containing MacConkey agar for enumeration of the colony forming units. The absence of specific antibodies for the ExPEC strains used in this study was confirmed by in vitro agglutination tests.
AnimalsAdult male Swiss mice weighing approximately 35g, obtained from Keizo-Azami Immunopathology Laboratory (LIKA/UFPE), were used. The animals were kept in an animal house with free access to water and commercial sterile diet (Purina, Paulínia, SP, Brazil). The mice were handled according to established experimental procedures.
Experimental infection with selected ExPEC strainsThe mice were separated into three groups (n=5) and challenged by the intraperitoneal (i.p.) route with 0,2mL of bacterial suspensions containing 106CFU/mL. Experimental infections were carried out with strains 4A, 41A and 2B. Clinical symptoms such as prostration, weight loss and mortality were observed daily for seven days post-infection. Survivors were sacrificed under anesthesia with Halothane (Halocarbon Laboratories, USA). Sections of the liver were submitted to enumeration of colony forming units (CFU/g) and histological examination.
Enumeration of colony forming unitsThe spleens and livers were dissected, weighed and macerated in PBS (1:10 or 1:100, w/v) under sterile conditions. Serial decimal dilutions were made and 0,1mL aliquots were plated onto MacConkey agar (Oxoid). The colonies were counted after incubation at 37°C for 24h and the results expressed as CFU/g of organ.
Histological examinationTissues were fixed in 10% formaldehyde and processed for paraffin embedding. The sections (5μm) were stained with hematoxylin–eosin and the slides were coded and examined by a single pathologist, who was unaware of the experimental conditions of each group.
Statistical analysesThe statistical significance of data was assessed by analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by Student's t-test. The level of significance was determined as p<0,05.
ResultsThe antimicrobial resistance-susceptibility profiles of 27 extraintestinal pathogenic E. coli strains from carcasses of healthy and diseased poultry are shown in Table 3. The majority of ExPEC were resistant to at least four antibiotics from different classes. The most prevalent phenotypes were resistant to levofloxacin (51.8%), amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (70.4%), ampicillin (81.5%), cefalotin (88.8%), tetracycline (100%) and streptomycin (100%). The overall multidrug resistance varied from 4 to 11 antimicrobials and reached 92.6% of E. coli strains. In addition, 40.7% were simultaneously resistant to streptomycin, levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin and tetracycline. The proportion of highly multidrug resistant strains (8–11 antimicrobials) reached 22.2%. Conversely, the aminoglycoside amikacin of avian and human use were very effective against 89.9% of ExPEC. The MIC and MBC of typical antimicrobials used in Brazilian farms were determined for those ExPEC strains resistant to at least 4 antimicrobials. The level of resistance against doxycycline, neomycin, enrofloxacin and oxytetracycline reached, respectively, 88.0%, 100%, 75% and 91.7% of the strains (Table 4).
Resistance-susceptibility profiles of ExPEC strains to antimicrobials of avian or human use in Brazil.
| Antimicrobial class | Antimicrobials | Disc content (μg) | Use:avian (A)human (H) | Resistance breakpoint (mm) | Healthy carcasse | Diseased carcasse | Overall Resistance %b | Resistant strains | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S %a | I % | R % | S % | I % | R % | |||||||
| Penicillin | Ampicillin | 10 | A/H | ≤13 | 11.2 | 5,5 | 83.3 | 11.3 | 11 | 77.7 | 81.5 | 44A, 15C, 48B,36A, 43A, 5B,21C, 42C, 35,31C, 52B, 55B,5A, 24A, 54B,6 60A, 38B, 37B,3 39B, 46, 41A,2 2B |
| Aminoglycoside | Amikacin | 30 | A/H | ≤14 | 72.4 | 11 | 16.6 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 1,1 | 36A, 42B, 2B |
| Gentamicin | 10 | A/H | ≤12 | 61.3 | 11 | 27.7 | 56.6 | 0 | 44.4 | 33.3 | 32, 48B, 52B,55B, 42B, 54B,37B, 41A, 2B | |
| Streptomycin | 10 | H | ≤11 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 4A, 48A, 32,44A, 15C, 30C,48B, 36A, 43A,5B, 21C, 42C,35, 31C, 52B,55B, 5A, 42B,24A, 54B, 60A,38B, 37B, 39B,46, 41A, 2B | |
| Fluoroquinolone | Ciprofloxacin | 5 | A/H | ≤15 | 22.3 | 27.7 | 50 | 67.7 | 0 | 33.3 | 44.4 | 30C, 43A, 35,42B, 24A, 60A,38B, 37B, 39B,46, 41A, 2B |
| Levofloxacin | 5 | H | ≤13 | 27.9 | 11 | 61.1 | 55.6 | 11.1 | 33.3 | 51.8 | 15C, 30C, 43A,42C, 35, 5A, 42B, 24A, 60A,38B, 37B, 46,41A, 2B | |
| Phenicol | Chloramphenicol | 30 | A/H | ≤12 | 66.8 | 5,5 | 27.7 | 88.9 | 11.1 | 0 | 18.5 | 37B, 39B, 46,41A, 2B |
| Cephalosporin | Ceftazidim | 30 | H | ≤14 | 56.7 | 27.7 | 16.6 | 66.7 | 22.2 | 11.1 | 14.8 | 54B, 39B, 46,41A |
| Cefalotin | 30 | H | ≤14 | 5,7 | 5,5 | 88.8 | 0 | 11.1 | 88.9 | 88.8 | 32, 44A, 15C,30C, 48B, 36A,43A, 5B, 21C,42C, 31C, 52B,55B, 5A, 42B,24A, 54B, 60A,38B, 37B, 39B,46, 41A, 2B | |
| Carbapenem | Imipenem | 10 | H | ≤13 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Tetracycline | Tetracycline | 30 | A/H | ≤14 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 4A, 48A, 32,44A, 15C, 30C,48B, 36A, 43A,5B, 21C, 42C,35, 31C, 52B,55B, 5A, 42B,24A, 54B, 60A,38B, 37B, 39B,46, 41A, 2B |
| Monobactam | Aztreonam | 30 | H | ≤15 | 33.8 | 22.2 | 44 | 44.5 | 44.4 | 11.1 | 33.3 | 5B, 21C, 31C,5A, 54B, 38B,9B, 46, 41A,2B |
| Beta-lactam/beta-lactamase inhibitor | Amoxycillin/clavulanic acid | 20/10 | H | ≤13 | 22.3 | 5,5 | 72.2 | 33.4 | 0 | 66.6 | 70.4 | 44A, 36A, 5B,21C, 42C, 35,31C, 52B, 55B,5A, 24A, 54B,60A, 38B, 37B,39B, 46, 41A,2B |
Resistance of multidrug resistant ExPEC strains from poultry carcasses to antimicrobials commonly used in Brazilian farms.
| Strain | Antimicrobials (μg/mL) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Doxycycline | Neomycin | Enrofloxacin | Oxytetracycline | |||||
| MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | |
| 4A | 125 | – | >1000 | – | 1,9 | 31.2 | >1000 | – |
| 48A | 31.2 | – | >1000– | – | 1,9 | 250 | >1000 | – |
| 32 | >1000 | – | 500 | 500 | 62.5 | 1000 | 250 | 250 |
| 44A | 62.5 | 500 | >1000 | – | 15.6 | 250 | >1000 | – |
| 15C | 62.5 | 1000 | >1000 | – | 62.5 | – | 500 | – |
| 30C | 1,9 | 250 | 500 | 500 | 1,9 | 1,9 | 1,9 | 500 |
| 48B | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 1,9 | 62.5 | >1000 | – |
| 36A | 1,9 | 500 | 250 | 500 | 1,9 | 500 | >1000 | – |
| 43A | 62.5 | 500 | 62.5 | 250 | 31.2 | 250 | 250 | – |
| 5B | 62.5 | 500 | >1000 | – | 1,9 | 1000 | 250 | – |
| 21C | 125 | 500 | 500 | 1000 | 15.6 | – | 500 | 500 |
| 42C | 31.2 | – | 125 | 250 | 3,9 | 500 | 1000 | – |
| 35 | 125 | 250 | 500 | 500 | 31.2 | – | 62.5 | 500 |
| 31C | 125 | 500 | 250 | 250 | 15.6 | 1000 | >1000 | – |
| 52B | 31.2 | – | 500 | – | 7,8 | 500 | 500 | – |
| 55B | 62.5 | 1000 | >1000 | – | 31.2 | 1000 | 250 | – |
| 24A | 62.5 | 250 | >1000 | – | 125 | – | >1000 | – |
| 54B | 62.5 | 250 | >1000 | – | >1000 | – | 7,8 | 7,8 |
| 60A | 62.5 | 500 | >1000 | – | 15.6 | 1000 | 125 | – |
| 38B | 125 | 125 | >1000 | – | 62.5 | 125 | 125 | 125 |
| 37B | 62.5 | 125 | >1000 | – | 31.2 | 62.5 | 62.5 | – |
| 39B | 15.6 | 62.5 | 500 | 500 | 7,8 | 7,8 | >1000 | – |
| 46 | 62.5 | 125 | 500 | 500 | 31.2 | 250 | >1000 | – |
| 41A | 62.5 | 62.5 | >1000 | – | NT | NT | NT | NT |
| 2B | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 31.2 | 31.2 | 1000 | – |
| Resistance breakpoint | ≥16 | ≥32 | ≥2 | ≥16 | ||||
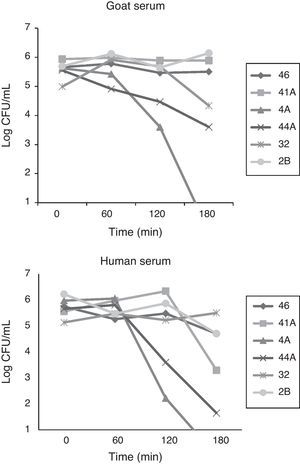
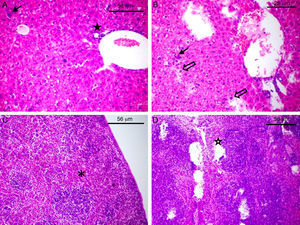
The complement resistance to goat serum was high for strains 2B and 46 and low for strains 4A and 41A, whereas resistance to human serum was high for strains 32, 46 and 2B and low for strains 44 and 4A (Fig. 1). Experiments carried out with laboratory animals have shown that Swiss mice challenged with strains 4A, 41A and 2B can survive seven days after infection. After this time, the bacterial load in the spleen and the liver reached respectively: 3,74×103 and 8,54×103CFU/g for strain 4A; 4,8×102 and 1,56×103CFU/g for strain 41A, and 4,0×101 and 1,2×104CFU/g for strain 2B. However, strain 2B provoked severe degeneration of hepatocytes besides lymphocytic and lipid infiltration in the liver, whereas spleen showed areas of degeneration of the white and red pulp (Fig. 2B and D). Likewise, the liver of mice challenged with strain 41A showed marked vacuolization of hepatocytes and lymphocytic infiltration, whereas the spleen showed leukocyte infiltration and white pulp without boundaries (data not shown). Conversely, strain 4A showed hepatocytes, portal space and lobular veins preserved with mild lymphocytic infiltration in the liver. Also, the spleen was morphologically preserved with capsule, and white pulp with central arteriole besides red pulp (Fig. 2A and C). These histological findings were generally perceptible in all mice from each animal group independently of the bacterial load in the organs.
Histological damage to laboratory animals after challenge with avian ExPEC. The slides of the liver (A and B) and spleen (C and D) of Swiss mice challenged with strain 4A (A and C) and 2B (B and D) are shown. The full arrow (A and B) indicates leukocyte infiltration whereas empty arrow shows degeneration of hepatocytes (B). The full star shows portal space (A) and empty star shows degeneration of red besides white pulp (D). The asterisk shows the white pulp of the spleen in normal morphology (C).
Poultry-associated diseases caused by ExPEC cause massive economic losses in the food industry.18–20 However, the broad use of antimicrobials by poultry farmers in recent decades has led to the emergence of multidrug resistant strains in many parts of the globe.21–24 Additionally, among multidrug resistant E. coli from chickens and piglets in China, 97% harbored the iss gene, suggesting this gene could also be used as a multidrug resistance marker.22 In Brazil, a previous study showed that the rates of multidrug resistance among avian E. coli reached 77.5%.25 Regarding ExPEC strains harboring the iss gene, we confirmed that the majority were resistant to several antimicrobials beyond those authorized for inclusion in broiler feed. Although the number of strains investigated was small, the levels of antimicrobial resistance to ampicillin, gentamicin, streptomycin, ciprofloxacin, chlorramphenicol and tetracycline were very high in comparison to the levels found in a recent study carried out with 101 E. coli strains from broilers and layer hens with colibacillosis infections in Bangladesh.26
Additionally, we have shown that a great number of avian ExPEC are probably β-lactamase producing strains, since resistance to amoxycillin/clavulanic acid was present in 70.4% of the isolates. Oteo et al.27 reported that resistance to amoxicillin-clavulanic acid is increasing among E. coli from human origin in Spanish hospitals, affecting 5,1% of 9090 blood isolates. Considering the food-chain, it is worrying that the only inhibitory drug against all avian ExPEC is carbapenem imipinem, restricted to human use. Also of particular concern are the resistance of avian ExPEC to fluoroquinoles such as enrofloxacin, which are similar to antibiotics being used in human medicine.28 For instance, the increasing resistance of E. coli strains to ciprofloxacin has been detected in several international studies.29,30 Enrofloxacin has been withdrawal from non-therapeutic use in the poultry industry in the United States.31 In Europe, the drug cannot be used in the animals from which eggs are produced for human consumption.32 However, in this study the level of antimicrobial resistance to doxycycline, neomycin, enrofloxacin and oxytetracycline reached alarming levels. Although we cannot confirm that Brazilian farmers restrict their use of such antimicrobials to treatment regimens, it was clear that these drugs should no longer be used on Brazilian poultry farms.
Avian ExPEC strains have been genetically associated with human E. coli causing urinary infections.6 Additionally, E. coli strains of the EcoR group B2 related to human and animal extraintestinal infections have been detected among APEC strains obtained from diseased and healthy chickens.33 In spite of the implications of avian ExPEC in carcasses of healthy poultry is unclear, a previous study in the UK showed that samples of imported chicken breasts were often positive for E. coli with CTX-M-2 genotype related to human infections in South America.34 Our data shows that resistance of avian E. coli to serum complement lyses in mammalian hosts was not directly related to the presence of the iss gene. This finding suggests that other genetic determinants among E. coli of avian origin must be related to human serum resistance. Additionally, multidrug-resistant ExPEC strains 41A and 2B were often more resistant to goat and human serum complement, and also more virulent to the experimentally infected mice than strain 4A, which is sensitive to the majority of antimicrobials.
Previous studies have shown the correlation between serum resistance and virulence of E. coli causing diseases in turkeys and chickens.35 Moreover, the characterization a transferable hybrid plasmid pAPEC-O103-ColBM encoding multidrug resistance and pathogenicity was recently described.11 Even though virulence and multidrug resistance genes are not uniformly distributed among conjugative plasmids, the diversity of avian ExPEC with zoonotic potential to cause human diseases can be more frequent than perceived. For example, in the present study the risk for human health was particularly observed for strain 2B, obtained from poultry carcasses approved for human consumption. Thus, an early diagnosis procedure should be followed on poultry farms and at slaughterhouses to identify hazardous microorganisms in asymptomatic poultry, and therefore eliminate carcasses that are not proper for human consumption. The data reinforce the general concern about the spread of multidrug-resistance and virulence genes between avian and human E. coli through the food-chain.
Conflict of interestThe authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
The authors thank the Brazilian Council of Research (CNPq) for research funding. Prof. Lima-Filho was supported by a Scholarship funding from Programa de Educação Tutorial (PET-MEC/SESu). The authors also thank Maria Helena (LIKA/UFPE) for providing the laboratory animals used in this study.