A total of 2484 target bacterial pathogens were collected (one per patient episode) from patients in 16 Latin American medical centers located in seven nations during 2011. Isolate identity was confirmed at a coordinating laboratory and susceptibility testing was performed for ceftaroline and comparator agents according to reference broth microdilution methods. A total of 30.0% of isolates were from respiratory tract, 29.4% from skin and skin structure, 21.4% from blood stream, 7.9% from urinary tract and 11.3% from other sites. Ceftaroline was active against Staphylococcus aureus (42.8% MRSA) with 83.6% of the isolates at ≤1mg/L and all isolates at ≤2mg/L (MIC5090, 0.25/2mg/L). National MRSA rates ranged from a low of 28.8% in Colombia to a high of 68.1% in Chile. All Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus agalactiae were susceptible to ceftaroline (MIC50/90 values were at ≤0.015/≤0.015mg/L for both). All Streptococcus pneumoniae were susceptible to ceftaroline, linezolid, tigecycline and vancomycin. Susceptibility to ceftriaxone was at 88.4% (CLSI non-meningitis interpretive criteria) and 73.9% (CLSI meningitis interpretive criteria) for all S. pneumoniae. Ceftriaxone susceptibility was only at 33.3% (CLSI non-meningitis interpretive criteria) and 0.0% (CLSI meningitis interpretive criteria) for penicillin-intermediate (penicillin MIC, 4mg/L) strains. All Haemophilus influenzae (29.4% β-lactamase-positive) isolates were susceptible to ceftaroline, amoxicillin–clavulanate, ceftriaxone, and levofloxacin. For the Latin American region, the ESBL-phenotype rate was 37.6% for Escherichia coli and 53.3% for Klebsiella pneumoniae. Ceftaroline was not active against ESBL-phenotype strains but was active against >90.0% of the non-ESBL-phenotype. The spectrum of activity of ceftaroline against pathogens from Latin America indicates that it merits further study for its potential use in the Latin American region.
Ceftaroline fosamil (the prodrug of the active metabolite ceftaroline) is a new cephalosporin approved in the USA in 2010 for acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections and community-acquired bacterial pneumonia and in Europe in 2012 for community-acquired pneumonia and complicated skin and soft tissue infections.1,2 It was shown that ceftaroline fosamil was non-inferior to comparator agents in clinical studies of the above indications.3–6 Ceftaroline is a bactericidal agent that exhibits broad in vitro activity against Staphylococcus aureus including methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus spp., and Enterobacteriaceae.7–13 Ceftaroline exhibits a level of binding affinity for PBPs in S. aureus including PBP2a in MRSA and in S. pneumoniae including PBP2B and 2X.7,8
Ceftaroline and comparator agent activities against pathogens have been monitored since 2008 in the Assessing Worldwide Antimicrobial Resistance Evaluation (AWARE) Program.10–13 The program provides continuing longitudinal data on antimicrobial activity in order to provide contemporary information. In this report, we present the results of the Latin American regional surveillance program for 2484 target pathogens from 16 medical centers from seven countries collected during 2011 from SENTRY as part of the AWARE program.
Materials and methodsOrganism collectionA total of 2484 target bacterial pathogens (S. aureus, S. pneumoniae, S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, Group C streptococci, Haemophilus influenzae, Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella oxytoca, and Morganella morganii) were collected (one per patient episode) from patients in Latin American medical centers during 2011. Isolates were obtained from specimens of patients with respiratory tract infections (30.0%), skin and skin structure infections, e.g. wound swabs or aspirated pus, etc. (29.4%), bloodstream infections (21.4%), urinary tract infections (7.9%), and other infection types (11.3%; includes bone/joint, central nervous system, ear/nose/throat, eye, genital tract, and intra-abdominal infections). Isolate identity was confirmed at the coordinating laboratory (JMI Laboratories, North Liberty, IA, USA). Sixteen medical centers participated from seven nations (nation [number of medical centers]): Argentina (2), Brazil (5), Chile (2) Colombia (1), Mexico (3), Panama (1), and Venezuela (2).
Susceptibility testingBacterial isolates were tested for susceptibility to ceftaroline and comparator agents according to the reference broth microdilution methods of the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI).14 Susceptibility interpretations were based on CLSI (M100-S23) or EUCAST (2013) criteria; in the case of tigecycline the USA-FDA drug package insert criteria were used in lieu of CLSI criteria, as no CLSI interpretive criteria for tigecycline exist.15–17 CLSI interpretive criteria for S. aureus for ceftaroline are susceptible, ≤1mg/L; intermediate, 2mg/L; resistant, ≥4mg/L while EUCAST interpretive criteria are susceptible, ≤1mg/L and resistant, >1mg/L. Discussions on susceptibility presented in this report are based on CLSI interpretations unless otherwise specified. Cation-adjusted Mueller-Hinton broth (CA-MHB), supplemented with 2.5–5% lysed horse blood for streptococci, was used for susceptibility testing. For Haemophilus spp., Haemophilus Test Medium was used.14E. coli and Klebsiella spp. isolates were grouped as “ESBL-phenotype” based on the CLSI screening criteria for ESBL production, i.e. MIC of ≥2mg/L for ceftazidime or ceftriaxone or aztreonam.15 Concurrent quality control (QC) testing was performed. QC strains included: S. aureus ATCC 29213, Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212, S. pneumoniae ATCC 49619, H. influenzae ATCC 49247 and 49766, E. coli ATCC 25922 and 35218, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853. All QC results were within published CLSI ranges.15
ResultsThe following numbers of organisms were collected from the 16 participating medical centers: S. aureus (956), S. pneumoniae (249), S. pyogenes (66), Streptococcus agalactiae (78), Group C streptococcus (5), H. influenzae (126), H. parainfluenzae (6), E. coli (518), K. pneumoniae (379), K. oxytoca (40), and M. morganii (61). Thirty percent were from respiratory tract, 29.4% from skin and skin structure, 21.4% from blood stream, 7.9% from urinary tract, and 11.3% from other sites.
Ceftaroline was active against S. aureus with MICs for 83.6% of the isolates at ≤1mg/L and all isolates at ≤2mg/L (MIC50/90, 0.25/2mg/L; Table 1). Ceftaroline was four- to eight-fold more active against MSSA (MIC50 and MIC90, 0.25 and 0.25mg/L) than MRSA (MIC50 and MIC90, 1 and 2mg/L). A total of 42.8% of S. aureus were MRSA (Tables 1 and 2). For MRSA, the MIC50/90 values for ceftaroline were 1/2mg/L with 61.6% of MIC values at ≤1mg/L (Tables 1 and 2). Ceftaroline was 16-fold more active than ceftriaxone against MSSA (data not shown). By definition all MRSA are resistant to ceftriaxone and all other β-lactams except for the anti-MRSA cephalosporin ceftaroline.15,16 National MRSA rates ranged from a low of 28.8% in Colombia to a high of 68.1% in Chile (Table 3). All S. aureus were susceptible to daptomycin, linezolid, tigecycline, and vancomycin (Table 2).
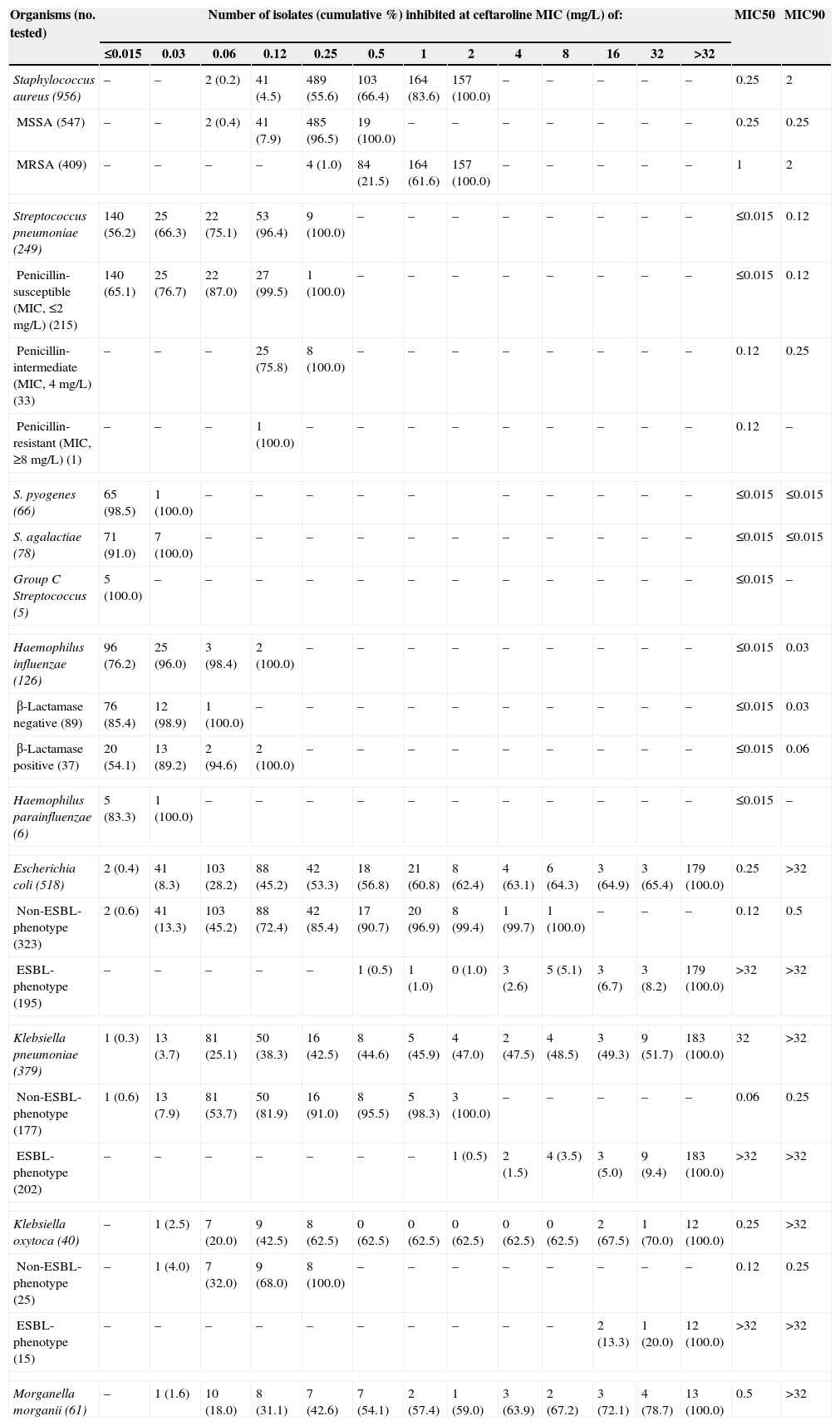
Summary of ceftaroline activity tested against pathogen groups from Latin America (2011).
| Organisms (no. tested) | Number of isolates (cumulative %) inhibited at ceftaroline MIC (mg/L) of: | MIC50 | MIC90 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤0.015 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | >32 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus (956) | – | – | 2 (0.2) | 41 (4.5) | 489 (55.6) | 103 (66.4) | 164 (83.6) | 157 (100.0) | – | – | – | – | – | 0.25 | 2 |
| MSSA (547) | – | – | 2 (0.4) | 41 (7.9) | 485 (96.5) | 19 (100.0) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| MRSA (409) | – | – | – | – | 4 (1.0) | 84 (21.5) | 164 (61.6) | 157 (100.0) | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | 2 |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae (249) | 140 (56.2) | 25 (66.3) | 22 (75.1) | 53 (96.4) | 9 (100.0) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | ≤0.015 | 0.12 |
| Penicillin-susceptible (MIC, ≤2mg/L) (215) | 140 (65.1) | 25 (76.7) | 22 (87.0) | 27 (99.5) | 1 (100.0) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | ≤0.015 | 0.12 |
| Penicillin-intermediate (MIC, 4mg/L) (33) | – | – | – | 25 (75.8) | 8 (100.0) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0.12 | 0.25 |
| Penicillin-resistant (MIC, ≥8mg/L) (1) | – | – | – | 1 (100.0) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0.12 | – |
| S. pyogenes (66) | 65 (98.5) | 1 (100.0) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | ≤0.015 | ≤0.015 | |
| S. agalactiae (78) | 71 (91.0) | 7 (100.0) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | ≤0.015 | ≤0.015 |
| Group C Streptococcus (5) | 5 (100.0) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | ≤0.015 | – |
| Haemophilus influenzae (126) | 96 (76.2) | 25 (96.0) | 3 (98.4) | 2 (100.0) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | ≤0.015 | 0.03 |
| β-Lactamase negative (89) | 76 (85.4) | 12 (98.9) | 1 (100.0) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | ≤0.015 | 0.03 |
| β-Lactamase positive (37) | 20 (54.1) | 13 (89.2) | 2 (94.6) | 2 (100.0) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | ≤0.015 | 0.06 |
| Haemophilus parainfluenzae (6) | 5 (83.3) | 1 (100.0) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | ≤0.015 | – |
| Escherichia coli (518) | 2 (0.4) | 41 (8.3) | 103 (28.2) | 88 (45.2) | 42 (53.3) | 18 (56.8) | 21 (60.8) | 8 (62.4) | 4 (63.1) | 6 (64.3) | 3 (64.9) | 3 (65.4) | 179 (100.0) | 0.25 | >32 |
| Non-ESBL-phenotype (323) | 2 (0.6) | 41 (13.3) | 103 (45.2) | 88 (72.4) | 42 (85.4) | 17 (90.7) | 20 (96.9) | 8 (99.4) | 1 (99.7) | 1 (100.0) | – | – | – | 0.12 | 0.5 |
| ESBL-phenotype (195) | – | – | – | – | – | 1 (0.5) | 1 (1.0) | 0 (1.0) | 3 (2.6) | 5 (5.1) | 3 (6.7) | 3 (8.2) | 179 (100.0) | >32 | >32 |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae (379) | 1 (0.3) | 13 (3.7) | 81 (25.1) | 50 (38.3) | 16 (42.5) | 8 (44.6) | 5 (45.9) | 4 (47.0) | 2 (47.5) | 4 (48.5) | 3 (49.3) | 9 (51.7) | 183 (100.0) | 32 | >32 |
| Non-ESBL-phenotype (177) | 1 (0.6) | 13 (7.9) | 81 (53.7) | 50 (81.9) | 16 (91.0) | 8 (95.5) | 5 (98.3) | 3 (100.0) | – | – | – | – | – | 0.06 | 0.25 |
| ESBL-phenotype (202) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 (0.5) | 2 (1.5) | 4 (3.5) | 3 (5.0) | 9 (9.4) | 183 (100.0) | >32 | >32 |
| Klebsiella oxytoca (40) | – | 1 (2.5) | 7 (20.0) | 9 (42.5) | 8 (62.5) | 0 (62.5) | 0 (62.5) | 0 (62.5) | 0 (62.5) | 0 (62.5) | 2 (67.5) | 1 (70.0) | 12 (100.0) | 0.25 | >32 |
| Non-ESBL-phenotype (25) | – | 1 (4.0) | 7 (32.0) | 9 (68.0) | 8 (100.0) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0.12 | 0.25 |
| ESBL-phenotype (15) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 2 (13.3) | 1 (20.0) | 12 (100.0) | >32 | >32 |
| Morganella morganii (61) | – | 1 (1.6) | 10 (18.0) | 8 (31.1) | 7 (42.6) | 7 (54.1) | 2 (57.4) | 1 (59.0) | 3 (63.9) | 2 (67.2) | 3 (72.1) | 4 (78.7) | 13 (100.0) | 0.5 | >32 |
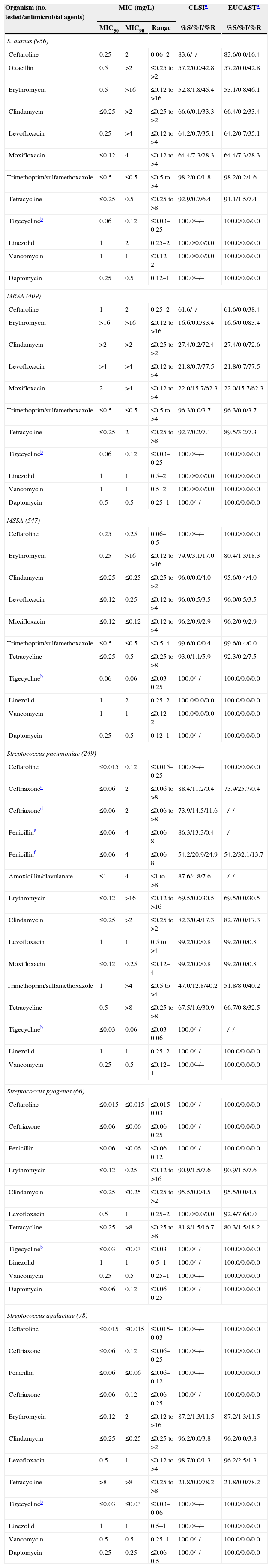
Activity of ceftaroline and comparator antimicrobial agents when tested against contemporary Gram-positive pathogens from Latin American medical centers (2011).
| Organism (no. tested/antimicrobial agents) | MIC (mg/L) | CLSIa | EUCASTa | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC50 | MIC90 | Range | %S/%I/%R | %S/%I/%R | |
| S. aureus (956) | |||||
| Ceftaroline | 0.25 | 2 | 0.06–2 | 83.6/–/– | 83.6/0.0/16.4 |
| Oxacillin | 0.5 | >2 | ≤0.25 to >2 | 57.2/0.0/42.8 | 57.2/0.0/42.8 |
| Erythromycin | 0.5 | >16 | ≤0.12 to >16 | 52.8/1.8/45.4 | 53.1/0.8/46.1 |
| Clindamycin | ≤0.25 | >2 | ≤0.25 to >2 | 66.6/0.1/33.3 | 66.4/0.2/33.4 |
| Levofloxacin | 0.25 | >4 | ≤0.12 to >4 | 64.2/0.7/35.1 | 64.2/0.7/35.1 |
| Moxifloxacin | ≤0.12 | 4 | ≤0.12 to >4 | 64.4/7.3/28.3 | 64.4/7.3/28.3 |
| Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole | ≤0.5 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.5 to >4 | 98.2/0.0/1.8 | 98.2/0.2/1.6 |
| Tetracycline | ≤0.25 | 0.5 | ≤0.25 to >8 | 92.9/0.7/6.4 | 91.1/1.5/7.4 |
| Tigecyclineb | 0.06 | 0.12 | ≤0.03–0.25 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Linezolid | 1 | 2 | 0.25–2 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Vancomycin | 1 | 1 | ≤0.12–2 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Daptomycin | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.12–1 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| MRSA (409) | |||||
| Ceftaroline | 1 | 2 | 0.25–2 | 61.6/–/– | 61.6/0.0/38.4 |
| Erythromycin | >16 | >16 | ≤0.12 to >16 | 16.6/0.0/83.4 | 16.6/0.0/83.4 |
| Clindamycin | >2 | >2 | ≤0.25 to >2 | 27.4/0.2/72.4 | 27.4/0.0/72.6 |
| Levofloxacin | >4 | >4 | ≤0.12 to >4 | 21.8/0.7/77.5 | 21.8/0.7/77.5 |
| Moxifloxacin | 2 | >4 | ≤0.12 to >4 | 22.0/15.7/62.3 | 22.0/15.7/62.3 |
| Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole | ≤0.5 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.5 to >4 | 96.3/0.0/3.7 | 96.3/0.0/3.7 |
| Tetracycline | ≤0.25 | 2 | ≤0.25 to >8 | 92.7/0.2/7.1 | 89.5/3.2/7.3 |
| Tigecyclineb | 0.06 | 0.12 | ≤0.03–0.25 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Linezolid | 1 | 1 | 0.5–2 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Vancomycin | 1 | 1 | 0.5–2 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Daptomycin | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.25–1 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| MSSA (547) | |||||
| Ceftaroline | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.06–0.5 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Erythromycin | 0.25 | >16 | ≤0.12 to >16 | 79.9/3.1/17.0 | 80.4/1.3/18.3 |
| Clindamycin | ≤0.25 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.25 to >2 | 96.0/0.0/4.0 | 95.6/0.4/4.0 |
| Levofloxacin | ≤0.12 | 0.25 | ≤0.12 to >4 | 96.0/0.5/3.5 | 96.0/0.5/3.5 |
| Moxifloxacin | ≤0.12 | ≤0.12 | ≤0.12 to >4 | 96.2/0.9/2.9 | 96.2/0.9/2.9 |
| Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole | ≤0.5 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.5–4 | 99.6/0.0/0.4 | 99.6/0.4/0.0 |
| Tetracycline | ≤0.25 | 0.5 | ≤0.25 to >8 | 93.0/1.1/5.9 | 92.3/0.2/7.5 |
| Tigecyclineb | 0.06 | 0.06 | ≤0.03–0.25 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Linezolid | 1 | 2 | 0.25–2 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Vancomycin | 1 | 1 | ≤0.12–2 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Daptomycin | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.12–1 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae (249) | |||||
| Ceftaroline | ≤0.015 | 0.12 | ≤0.015–0.25 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Ceftriaxonec | ≤0.06 | 2 | ≤0.06 to >8 | 88.4/11.2/0.4 | 73.9/25.7/0.4 |
| Ceftriaxoned | ≤0.06 | 2 | ≤0.06 to >8 | 73.9/14.5/11.6 | –/–/– |
| Penicilline | ≤0.06 | 4 | ≤0.06–8 | 86.3/13.3/0.4 | –/– |
| Penicillinf | ≤0.06 | 4 | ≤0.06–8 | 54.2/20.9/24.9 | 54.2/32.1/13.7 |
| Amoxicillin/clavulanate | ≤1 | 4 | ≤1 to >8 | 87.6/4.8/7.6 | –/–/– |
| Erythromycin | ≤0.12 | >16 | ≤0.12 to >16 | 69.5/0.0/30.5 | 69.5/0.0/30.5 |
| Clindamycin | ≤0.25 | >2 | ≤0.25 to >2 | 82.3/0.4/17.3 | 82.7/0.0/17.3 |
| Levofloxacin | 1 | 1 | 0.5 to >4 | 99.2/0.0/0.8 | 99.2/0.0/0.8 |
| Moxifloxacin | ≤0.12 | 0.25 | ≤0.12–4 | 99.2/0.0/0.8 | 99.2/0.0/0.8 |
| Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole | 1 | >4 | ≤0.5 to >4 | 47.0/12.8/40.2 | 51.8/8.0/40.2 |
| Tetracycline | 0.5 | >8 | ≤0.25 to >8 | 67.5/1.6/30.9 | 66.7/0.8/32.5 |
| Tigecyclineb | ≤0.03 | 0.06 | ≤0.03–0.06 | 100.0/–/– | –/–/– |
| Linezolid | 1 | 1 | 0.25–2 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Vancomycin | 0.25 | 0.5 | ≤0.12–1 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Streptococcus pyogenes (66) | |||||
| Ceftaroline | ≤0.015 | ≤0.015 | ≤0.015–0.03 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Ceftriaxone | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06–0.25 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Penicillin | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06–0.12 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Erythromycin | ≤0.12 | 0.25 | ≤0.12 to >16 | 90.9/1.5/7.6 | 90.9/1.5/7.6 |
| Clindamycin | ≤0.25 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.25 to >2 | 95.5/0.0/4.5 | 95.5/0.0/4.5 |
| Levofloxacin | 0.5 | 1 | 0.25–2 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 | 92.4/7.6/0.0 |
| Tetracycline | ≤0.25 | >8 | ≤0.25 to >8 | 81.8/1.5/16.7 | 80.3/1.5/18.2 |
| Tigecyclineb | ≤0.03 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.03 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Linezolid | 1 | 1 | 0.5–1 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Vancomycin | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.25–1 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Daptomycin | ≤0.06 | 0.12 | ≤0.06–0.25 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Streptococcus agalactiae (78) | |||||
| Ceftaroline | ≤0.015 | ≤0.015 | ≤0.015–0.03 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Ceftriaxone | ≤0.06 | 0.12 | ≤0.06–0.25 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Penicillin | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06–0.12 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Ceftriaxone | ≤0.06 | 0.12 | ≤0.06–0.25 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Erythromycin | ≤0.12 | 2 | ≤0.12 to >16 | 87.2/1.3/11.5 | 87.2/1.3/11.5 |
| Clindamycin | ≤0.25 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.25 to >2 | 96.2/0.0/3.8 | 96.2/0.0/3.8 |
| Levofloxacin | 0.5 | 1 | ≤0.12 to >4 | 98.7/0.0/1.3 | 96.2/2.5/1.3 |
| Tetracycline | >8 | >8 | ≤0.25 to >8 | 21.8/0.0/78.2 | 21.8/0.0/78.2 |
| Tigecyclineb | ≤0.03 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.03–0.06 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Linezolid | 1 | 1 | 0.5–1 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Vancomycin | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.25–1 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Daptomycin | 0.25 | 0.25 | ≤0.06–0.5 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
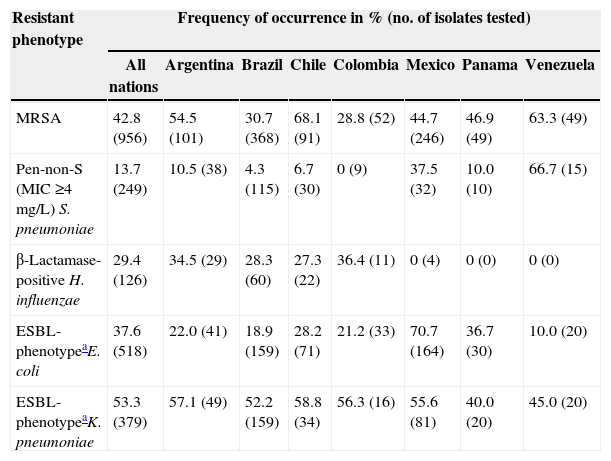
Antimicrobial resistant phenotypes stratified by nation.
| Resistant phenotype | Frequency of occurrence in % (no. of isolates tested) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All nations | Argentina | Brazil | Chile | Colombia | Mexico | Panama | Venezuela | |
| MRSA | 42.8 (956) | 54.5 (101) | 30.7 (368) | 68.1 (91) | 28.8 (52) | 44.7 (246) | 46.9 (49) | 63.3 (49) |
| Pen-non-S (MIC ≥4mg/L) S. pneumoniae | 13.7 (249) | 10.5 (38) | 4.3 (115) | 6.7 (30) | 0 (9) | 37.5 (32) | 10.0 (10) | 66.7 (15) |
| β-Lactamase-positive H. influenzae | 29.4 (126) | 34.5 (29) | 28.3 (60) | 27.3 (22) | 36.4 (11) | 0 (4) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| ESBL-phenotypeaE. coli | 37.6 (518) | 22.0 (41) | 18.9 (159) | 28.2 (71) | 21.2 (33) | 70.7 (164) | 36.7 (30) | 10.0 (20) |
| ESBL-phenotypeaK. pneumoniae | 53.3 (379) | 57.1 (49) | 52.2 (159) | 58.8 (34) | 56.3 (16) | 55.6 (81) | 40.0 (20) | 45.0 (20) |
ESBL-phenotype defined as MIC of ≥2mg/L for ceftazidime or ceftriaxone or aztreonam (CLSI, 2013).
The overall susceptibility of S. aureus to ceftaroline was 83.6% (Table 2). For MSSA, susceptibility to ceftaroline was 100.0% and for MRSA it was 61.6% (Table 2). All ceftaroline non-susceptible S. aureus isolates (16.4% of all S. aureus) were MRSA and exhibited a MIC value of 2mg/L (intermediate by CLSI criteria, resistant by EUCAST criteria) (Table 1). MRSA with a ceftaroline MIC at 2mg/L were found in all sampled countries and rates varied from country to country. The percent of MRSA isolates which exhibited a MIC of 2mg/L are listed for each country in rank order: Columbia (6.7%), Mexico (15.5%), Argentina (35.5%), Brazil (39.8%), Venezuela (41.9%), Panama (47.8%) and Chile (83.9%) (data not shown). Isolates with a ceftaroline MIC at 2mg/L were found in respiratory, skin and soft tissue, bloodstream, and other infection types.
All S. pyogenes and S. agalactiae were susceptible to ceftaroline and MIC50/90 values were at ≤0.015/≤0.015mg/L (Tables 1 and 2). S. pyogenes was highly susceptible to many other agents including ceftriaxone, penicillin, daptomycin, tigecycline, vancomycin and linezolid, each at 100.0% susceptibility (Table 2). However, susceptibility to tetracycline was only at 81.8% and erythromycin at 90.9% (Table 2). All isolates were susceptible to levofloxacin based on CLSI criteria; however, 7.6% of isolates were non-susceptible to levofloxacin based on EUCAST criteria (Table 2). All S. agalactiae were susceptible to all tested β-lactams, as well as daptomycin, linezolid, tigecycline and vancomycin (Table 2).
All S. pneumoniae were susceptible to ceftaroline, linezolid, tigecycline and vancomycin (Table 2). Susceptibility to erythromycin, tetracycline and trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole ranged from 47.0% to 69.5% (Table 2). Susceptibility to ceftriaxone was at 88.4% (CLSI non-meningitis interpretive criteria) or 73.9% (meningitis interpretive criteria) and at 73.9% when applying EUCAST criteria for all S. pneumoniae (Table 2). Susceptibility to ceftriaxone was only at 33.3% (non-meningitis interpretive criteria) and 0.0% when applying either CLSI interpretive criteria for meningitis or EUCAST criteria for penicillin-intermediate (penicillin MIC, 4mg/L) strains (data not shown). For ceftaroline, the MIC50/90 was at ≤0.015/0.12mg/L with the highest MIC value at 0.25mg/L. There was only one penicillin-resistant strain (penicillin MIC, ≥8mg/L) from Brazil which was resistant to erythromycin and susceptible to clindamycin (data not shown) and which had a ceftaroline MIC at 0.12mg/L. Overall 13.7% of S. pneumoniae tested as non-susceptible to penicillin (MIC ≥4mg/L; Tables 2 and 3). The percentage of isolates that tested as penicillin non-susceptible was at 10.5% or less in Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Colombia and Panama (Table 3). Mexico at 37.5% and Venezuela at 66.7% exhibited the two highest rates (Table 3).
All H. influenzae isolates were susceptible to ceftaroline, amoxicillin–clavulanate, ceftriaxone, and levofloxacin (Table 4). Applying EUCAST criteria, the susceptibility rates for the above agents were 96.0, 88.9, 99.2 and 100.0%, respectively. Tigecycline susceptibility (86.5%) and trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole (61.1%) were compromised (Table 4). A total of 29.4% of isolates were β-lactamase-positive (Tables 1, 3 and 4). Of the three nations for which >20 H. influenzae isolates were obtained, β-lactamase-positive rates were 27.3% (Chile), 28.3% (Brazil) and 34.5% (Argentina Table 3). There were only six H. parainfluenzae, half of which were resistant to trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole and all ceftaroline MIC values were at ≤0.03mg/L (Table 1).
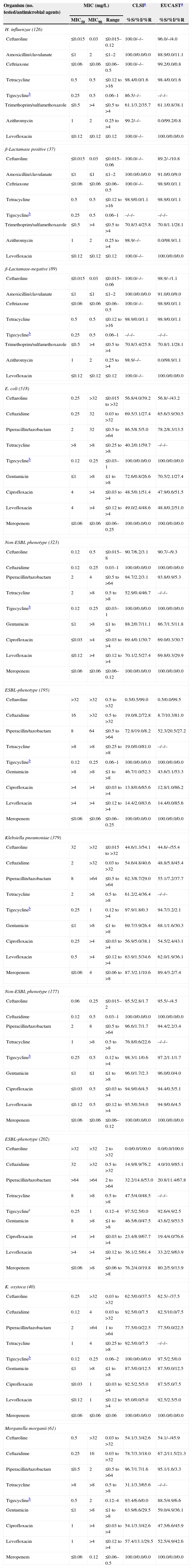
Activity of ceftaroline and comparator antimicrobial agents when tested against contemporary Gram-negative pathogens from Latin American medical centers (2011).
| Organism (no. tested/antimicrobial agents) | MIC (mg/L) | CLSIa | EUCASTa | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC50 | MIC90 | Range | %S/%I/%R | %S/%I/%R | |
| H. influenzae (126) | |||||
| Ceftaroline | ≤0.015 | 0.03 | ≤0.015–0.12 | 100.0/–/– | 96.0/–/4.0 |
| Amoxicillin/clavulanate | ≤1 | 2 | ≤1–2 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 | 88.9/0.0/11.1 |
| Ceftriaxone | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06–0.5 | 100.0/–/– | 99.2/0.0/0.8 |
| Tetracycline | 0.5 | 0.5 | ≤0.12 to >16 | 98.4/0.0/1.6 | 98.4/0.0/1.6 |
| Tigecyclineb | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.06–1 | 86.5/–/– | –/–/– |
| Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole | ≤0.5 | >4 | ≤0.5 to >4 | 61.1/3.2/35.7 | 61.1/0.8/38.1 |
| Azithromycin | 1 | 2 | 0.25 to >4 | 99.2/–/– | 0.0/99.2/0.8 |
| Levofloxacin | ≤0.12 | ≤0.12 | ≤0.12 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| β-Lactamase positive (37) | |||||
| Ceftaroline | ≤0.015 | 0.03 | ≤0.015–0.06 | 100.0/–/– | 89.2/–/10.8 |
| Amoxicillin/clavulanate | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1–2 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 | 91.0/0.0/9.0 |
| Ceftriaxone | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06–0.5 | 100.0/–/– | 98.9/0.0/1.1 |
| Tetracycline | 0.5 | 0.5 | ≤0.12 to >16 | 98.9/0.0/1.1 | 98.9/0.0/1.1 |
| Tigecyclineb | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.06–1 | –/–/– | –/–/– |
| Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole | ≤0.5 | >4 | ≤0.5 to >4 | 70.8/3.4/25.8 | 70.8/1.1/28.1 |
| Azithromycin | 1 | 2 | 0.25 to >4 | 98.9/–/– | 0.0/98.9/1.1 |
| Levofloxacin | ≤0.12 | ≤0.12 | ≤0.12 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| β-Lactamase-negative (89) | |||||
| Ceftaroline | ≤0.015 | 0.03 | ≤0.015–0.06 | 100.0/–/– | 98.9/–/1.1 |
| Amoxicillin/clavulanate | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1–2 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 | 91.0/0.0/9.0 |
| Ceftriaxone | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06–0.5 | 100.0/–/– | 98.9/0.0/1.1 |
| Tetracycline | 0.5 | 0.5 | ≤0.12 to >16 | 98.9/0.0/1.1 | 98.9/0.0/1.1 |
| Tigecyclineb | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.06–1 | –/–/– | –/–/– |
| Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole | ≤0.5 | >4 | ≤0.5 to >4 | 70.8/3.4/25.8 | 70.8/1.1/28.1 |
| Azithromycin | 1 | 2 | 0.25 to >4 | 98.9/–/– | 0.0/98.9/1.1 |
| Levofloxacin | ≤0.12 | ≤0.12 | ≤0.12 | 100.0/–/– | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| E. coli (518) | |||||
| Ceftaroline | 0.25 | >32 | ≤0.015 to >32 | 56.8/4.0/39.2 | 56.8/–/43.2 |
| Ceftazidime | 0.25 | 32 | 0.03 to >32 | 69.5/3.1/27.4 | 65.6/3.9/30.5 |
| Piperacillin/tazobactam | 2 | 32 | ≤0.5 to >64 | 86.5/8.5/5.0 | 78.2/8.3/13.5 |
| Tetracycline | >8 | >8 | ≤0.25 to >8 | 40.2/0.1/59.7 | –/–/– |
| Tigecyclineb | 0.12 | 0.25 | ≤0.03–1 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Gentamicin | ≤1 | >8 | ≤1 to >8 | 72.6/0.8/26.6 | 70.5/2.1/27.4 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 4 | >4 | ≤0.03 to >4 | 48.5/0.1/51.4 | 47.9/0.6/51.5 |
| Levofloxacin | 4 | >4 | ≤0.12 to >4 | 49.0/2.4/48.6 | 48.8/0.2/51.0 |
| Meropenem | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06–0.25 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Non-ESBL phenotype (323) | |||||
| Ceftaroline | 0.12 | 0.5 | ≤0.015–8 | 90.7/6.2/3.1 | 90.7/–/9.3 |
| Ceftazidime | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.03–1 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Piperacillin/tazobactam | 2 | 4 | ≤0.5 to >64 | 94.7/2.2/3.1 | 93.8/0.9/5.3 |
| Tetracycline | 2 | >8 | 0.5 to >8 | 52.9/0.4/46.7 | –/–/– |
| Tigecyclineb | 0.12 | 0.25 | ≤0.03–1 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Gentamicin | ≤1 | >8 | ≤1 to >8 | 88.2/0.7/11.1 | 86.7/1.5/11.8 |
| Ciprofloxacin | ≤0.03 | >4 | ≤0.03 to >4 | 69.4/0.1/30.7 | 69.0/0.3/30.7 |
| Levofloxacin | ≤0.12 | >4 | ≤0.12 to >4 | 70.1/2.5/27.4 | 69.8/0.3/29.9 |
| Meropenem | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06–0.12 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| ESBL-phenotype (195) | |||||
| Ceftaroline | >32 | >32 | 0.5 to >32 | 0.5/0.5/99.0 | 0.5/0.0/99.5 |
| Ceftazidime | 16 | >32 | 0.5 to >32 | 19.0/8.2/72.8 | 8.7/10.3/81.0 |
| Piperacillin/tazobactam | 8 | 64 | ≤0.5 to >64 | 72.8/19.0/8.2 | 52.3/20.5/27.2 |
| Tetracycline | >8 | >8 | ≤0.25 to >8 | 19.0/0.0/81.0 | –/–/– |
| Tigecyclineb | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.06–1 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Gentamicin | >8 | >8 | ≤1 to >8 | 46.7/1.0/52.3 | 43.6/3.1/53.3 |
| Ciprofloxacin | >4 | >4 | ≤0.03 to >4 | 13.8/0.6/85.6 | 12.8/1.0/86.2 |
| Levofloxacin | >4 | >4 | ≤0.12 to >4 | 14.4/2.0/83.6 | 14.4/0.0/85.6 |
| Meropenem | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06–0.25 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae (379) | |||||
| Ceftaroline | 32 | >32 | ≤0.015 to >32 | 44.6/1.3/54.1 | 44.6/–/55.4 |
| Ceftazidime | 2 | >32 | 0.03 to >32 | 54.6/4.8/40.6 | 48.8/5.8/45.4 |
| Piperacillin/tazobactam | 8 | >64 | ≤0.5 to >64 | 62.3/8.7/29.0 | 55.1/7.2/37.7 |
| Tetracycline | 2 | >8 | 0.5 to >8 | 61.2/2.4/36.4 | –/–/– |
| Tigecyclineb | 0.25 | 1 | 0.12 to >4 | 97.9/1.8/0.3 | 94.7/3.2/2.1 |
| Gentamicin | ≤1 | >8 | ≤1 to >8 | 69.7/3.9/26.4 | 68.1/1.6/30.3 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 0.25 | >4 | ≤0.03 to >4 | 56.9/5.0/38.1 | 54.5/2.4/43.1 |
| Levofloxacin | 0.5 | >4 | ≤0.12 to >4 | 63.9/1.5/34.6 | 62.0/1.9/36.1 |
| Meropenem | ≤0.06 | 4 | ≤0.06 to >8 | 87.3/2.1/10.6 | 89.4/3.2/7.4 |
| Non-ESBL phenotype (177) | |||||
| Ceftaroline | 0.06 | 0.25 | ≤0.015–2 | 95.5/2.8/1.7 | 95.5/–/4.5 |
| Ceftazidime | 0.12 | 0.5 | 0.03–1 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Piperacillin/tazobactam | 2 | 8 | ≤0.5 to >64 | 96.6/1.7/1.7 | 94.4/2.2/3.4 |
| Tetracycline | 1 | >8 | 0.5 to >8 | 76.8/0.6/22.6 | –/–/– |
| Tigecyclineb | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.12 to >4 | 98.3/1.1/0.6 | 97.2/1.1/1.7 |
| Gentamicin | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 to >8 | 96.0/1.7/2.3 | 96.0/0.0/4.0 |
| Ciprofloxacin | ≤0.03 | 0.5 | ≤0.03 to >4 | 94.9/0.6/4.5 | 94.4/0.5/5.1 |
| Levofloxacin | ≤0.12 | 0.5 | ≤0.12 to >4 | 95.5/0.5/4.0 | 94.9/0.6/4.5 |
| Meropenem | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06–0.12 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| ESBL-phenotype (202) | |||||
| Ceftaroline | >32 | >32 | 2 to >32 | 0.0/0.0/100.0 | 0.0/0.0/100.0 |
| Ceftazidime | 32 | >32 | 0.5 to >32 | 14.9/8.9/76.2 | 4.0/10.9/85.1 |
| Piperacillin/tazobactam | >64 | >64 | 2 to >64 | 32.2/14.8/53.0 | 20.8/11.4/67.8 |
| Tetracycline | 8 | >8 | 0.5 to >8 | 47.5/4.0/48.5 | –/–/– |
| Tigecyclinec | 0.25 | 1 | 0.12–4 | 97.5/2.5/0.0 | 92.6/4.9/2.5 |
| Gentamicin | 8 | >8 | ≤1 to >8 | 46.5/6.0/47.5 | 43.6/2.9/53.5 |
| Ciprofloxacin | >4 | >4 | ≤0.03 to >4 | 23.4/8.9/67.7 | 19.4/4.0/76.6 |
| Levofloxacin | >4 | >4 | ≤0.12 to >4 | 36.1/2.5/61.4 | 33.2/2.9/63.9 |
| Meropenem | ≤0.06 | >8 | ≤0.06 to >8 | 76.2/4.0/19.8 | 80.2/5.9/13.9 |
| K. oxytoca (40) | |||||
| Ceftaroline | 0.25 | >32 | 0.03 to >32 | 62.5/0.0/37.5 | 62.5/–/37.5 |
| Ceftazidime | 0.12 | 4 | 0.03 to >32 | 92.5/0.0/7.5 | 82.5/10.0/7.5 |
| Piperacillin/tazobactam | 2 | >64 | 1 to >64 | 77.5/0.0/22.5 | 77.5/0.0/22.5 |
| Tetracycline | 1 | 4 | ≤0.25 to >8 | 92.5/0.0/7.5 | –/–/– |
| Tigecyclineb | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.06–2 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 | 97.5/2.5/0.0 |
| Gentamicin | ≤1 | >8 | ≤1 to >8 | 87.5/0.0/12.5 | 87.5/0.0/12.5 |
| Ciprofloxacin | ≤0.03 | 1 | ≤0.03 to >4 | 92.5/2.5/5.0 | 87.5/5.0/7.5 |
| Levofloxacin | ≤0.12 | 1 | ≤0.12 to >4 | 95.0/0.0/5.0 | 92.5/2.5/5.0 |
| Meropenem | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
| Morganella morganii (61) | |||||
| Ceftaroline | 0.5 | >32 | 0.03 to >32 | 54.1/3.3/42.6 | 54.1/–/45.9 |
| Ceftazidime | 0.25 | 16 | 0.03 to >32 | 78.7/3.3/18.0 | 67.2/11.5/21.3 |
| Piperacillin/tazobactam | ≤0.5 | 2 | ≤0.5 to >64 | 96.7/1.7/1.6 | 95.1/1.6/3.3 |
| Tetracycline | >8 | >8 | 0.5 to >8 | 31.1/3.3/65.6 | –/–/– |
| Tigecyclineb | 0.5 | 2 | 0.12–4 | 93.4/6.6/0.0 | 88.5/4.9/6.6 |
| Gentamicin | ≤1 | >8 | ≤1 to >8 | 63.9/6.6/29.5 | 59.0/4.9/36.1 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 1 | >4 | ≤0.03 to >4 | 54.1/3.3/42.6 | 47.5/6.6/45.9 |
| Levofloxacin | 1 | >4 | ≤0.12 to >4 | 57.4/13.1/29.5 | 52.5/4.9/42.6 |
| Meropenem | ≤0.06 | 0.12 | ≤0.06–0.5 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 | 100.0/0.0/0.0 |
For the Latin American region, the ESBL-phenotype rate for 518 E. coli was 37.6% (Table 1). Only two nations demonstrated ESBL-phenotype rates of less than 20% (Venezuela [10.0%] and Brazil [18.9%]; Table 3). The highest rates were in Panama (36.7%) and Mexico (70.7%; Table 3). The regional ESBL-phenotype rate for K. pneumoniae (53.3%) was higher than the E. coli rate (Table 3). For K. pneumoniae, the lowest ESBL-phenotype rates were found in Panama (40.0%) and Venezuela (45.0%) with rates in the remaining five nations ranging from 52.2% to 58.8% (Table 3). All E. coli were susceptible to meropenem and tigecycline (Table 4). Susceptibility to piperacillin–tazobactam was at 86.5% (78.2% by EUCAST criteria; Table 4). However susceptibility of E. coli to the remaining agents ranged from a low 40.2% for tetracycline to a high 72.6% for gentamicin (Table 4). Susceptibilities were decreased further for the ESBL-phenotype strains of E. coli, where for example, levofloxacin susceptibility was at 14.4% (Table 4). For K. pneumoniae, tigecycline was the only agent tested which exhibited greater than 90% susceptibility (97.9%; 94.7% by EUCAST criteria; Table 4). As was noted for E. coli, the ESBL-phenotype strains of K. pneumoniae showed much higher resistance rates for most other agents; the exception was tigecycline, which still showed susceptibility at 97.5% (92.6% by EUCAST criteria; Table 4). Ceftaroline was not active against ESBL-phenotype strains of E. coli and K. pneumoniae; however 90.7% of non-ESBL-phenotype E. coli and 95.5% of non-ESBL-phenotype K. pneumoniae were susceptible to ceftaroline (Table 4).
DiscussionPrevious AWARE surveillance studies in the USA indicated that for S. aureus including MRSA the MIC90 for ceftaroline was at 1mg/L and the highest MIC values occurred in MRSA at 2mg/L.10,11,13 MRSA values at 2mg/L only represented 2.8% of MIC values for 9875 MRSA isolates collected during 2008–2011.13 In the Canadian surveillance program (CANWARD) with 15 sentinel hospital laboratories, the highest MIC value in the 2009 survey was at 0.5mg/L for MSSA and 1mg/L for MRSA.18 However, Farrell et al. showed that for isolates from 19 countries in Europe and the Mediterranean region although the MIC90 for S. aureus was 1mg/L, for MRSA, 11.2% of isolates were at 2mg/L.19 In this 2011 Latin American surveillance program, 16.4% of all S. aureus and 38.4% of MRSA exhibited a MIC value of 2mg/L. As was noted in the Europe and the Mediterranean region, there were more MRSA isolates with MIC values at 2mg/L than were noted in North America. This may be due to differences in circulating MRSA clones and would be reflected in the regional and local susceptibility patterns.20–22 For example, the highest percentage of MRSA with ceftaroline MIC of 2mg/L in our study was observed in Chile (83.9%) where previous studies had shown that the Cordobes/Chilean clone predominates.22 This clone displays the staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) type I which was shown to have a modal value for ceftaroline–avibactam of 2mg/L compared to 1mg/L for SCCmec types II and III and 0.5mg/L for SCCmec type IV.21
Overall β-streptococci were highly susceptible to ceftaroline and other commonly used agents. However, S. pneumoniae exhibited decreased susceptibility to a number of agents. For example, the overall rate of penicillin-non-susceptibility for S. pneumoniae (penicillin, MIC, ≥4mg/L) in the Latin American region was at 13.7% and varied on a national basis, up to 66.7% in Venezuela. Further, susceptibility of S. pneumoniae to ceftriaxone was at 88.4% (CLSI non-meningitis interpretive criteria) or 73.9% (CLSI meningitis interpretive criteria) for all S. pneumoniae (Table 2). Ceftriaxone susceptibility was decreased even more for penicillin-non-susceptible strains. Ceftaroline, which exhibited 100.0% susceptibility to all S. pneumoniae, may provide a potential alternative when penicillin or ceftriaxone non-susceptible isolates are a concern.
Ceftaroline was active against non-ESBL-phenotype Enterobacteriaceae; however as for third generation cephalosporins, it was not active against ESBL-phenotype strains. As the ESBL-phenotype occurred frequently in the Latin American region and varied among individual nations the likelihood of encountering a ESBL-phenotype strain will need to be considered in determining the potential role for ceftaroline. Examples of variation in national rates in this study included ESBL-phenotype E. coli isolates ranging from 10.0% (Venezuela) to 70.7% (Mexico) and for ESBL-phenotype K. pneumoniae national rates from 40.0% in Panama to 58.8% in Chile.
In summary, ceftaroline was shown to have in vitro activity against Gram-positive and selected Gram-negative pathogens isolated from patients in the Latin American region during 2011. The spectrum of activity for ceftaroline included key pathogens, which are found in a variety of infections including community-acquired pneumonia and skin and soft tissue infections. This included potent activity against non-ESBL producing E. coli and K. pneumoniae but a lack of activity against MDR Gram-negative bacteria such as ESBL-producing E. coli and K. pneumonia, which occurred frequently in the Latin American region. The spectrum of activity of ceftaroline against pathogens isolated from patients in Latin American medical centers indicates that it merits further study for its potential use in the region.
FundingThis study was funded by AstraZeneca, and JMI Laboratories received compensation fees for services in relation to preparing the manuscript, which was funded by AstraZeneca.
Conflicts of interestJMI Laboratories, Inc. has received research and educational grants in 2009–2012 from – American Proficiency Institute (API), Anacor, Astellas, Bayer, Cempra, Cerexa, Contrafect, Cubist, Daiichi, Dipexium, Enanta, Forest/Cerexa, Furiex, GlaxoSmithKline, Johnson & Johnson (Ortho McNeil), LegoChem Biosciences Inc., Meiji Seika Kaisha, Merck, Nabriva, Novartis, Pfizer (Wyeth), Rempex, Rib-X Pharmaceuticals, Seachaid, Shionogi, The Medicines Co., Theravance, ThermoFisher and some other corporations. Some JMI employees are advisors/consultants for Astellas, Cubist, Pfizer, Cempra, Cerexa-Forest, J&J, and Theravance. In regard to speakers bureaus and stock options – none to declare.