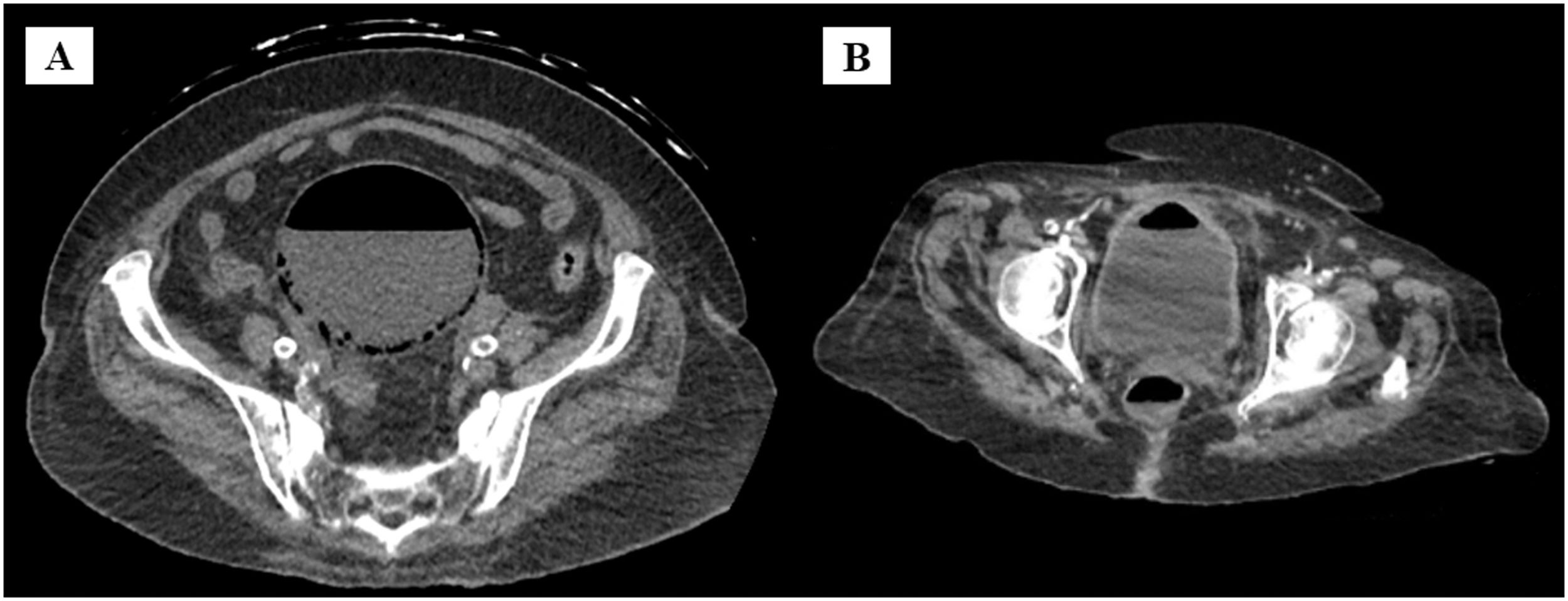
A 74-year-old woman was admitted to the emergency department reporting dysuria and hematuria for 20 days. She had diabetes mellitus and recurrent Urinary Tract Infections (UTI), as well as cervical cancer treated with radiotherapy 25 years ago. Physical examination revealed hypotension (92×60 mmHg), heart rate 112 bpm, axillary temperature 36.7 °C, abdominal pain, drowsiness and disorientation. Laboratory findings evidenced anemia and leukocytosis (Hb 6.8 g/d, white blood count 16.800 mm3), c-reative protein 288 mg/dL, creatinine 3.0 mg/dL, urea 136 mg/dL. The urinary analysis showed leukocyturia, hematuria and bacteriuria. Due to urinary sepsis, antibiotic therapy (cephtriaxone) was started, and hemodialysis was required. She was admitted to the intensive care unit. Urine culture isolated Klebsiella pneumoniae (100.000 UFC/mL) ciprofloxacin and amoxicillin clavulanate resistant and sensitive to the other antibiotics tested. Abdominal tomography revealed gas in the interior and walls of the bladder. A new tomography was performed after 14-days, and significant radiological improvement was noted. Since she had been through prolonged hospitalization and multiple sepsis, she developed critical neuropathy and was transferred to a special care unit, dying after forty (40) days of hospitalization. She remained on dialysis therapy throughout the period (Figure 1).
Emphysematous Cystitis (EC) is a rare form of Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) characterized by gas formation on the bladder walls. The incidence rate of EC reported among diabetic women is 91.5 per 1000 person-years for UTIs in general.1 The presentation includes: asymptomatic forms, classic cystitis up to sepsis.2 The most common agents are Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae.3 The main risk factors are Diabetes Mellitus (DM), female gender and neurogenic bladder.4 Clinical findings and imaging tests are important for the establishment of the correct diagnosis. Antibiotic therapy is the standard treatment. Prognosis is variable and early diagnosis favors better clinical evolution. Mortality varies between 7 %‒10 %.2,5
Informed consentInformed consent was obtained for publication of this case.
Authors' contributionAll authors contributed to data collection and discussed the final version of paper.