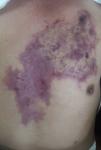
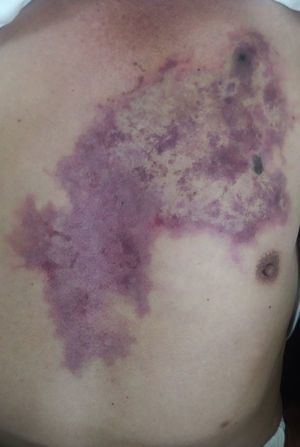
Loxoscelism is a disease caused by the bite of a spider of the genus Loxosceles, which causes a necrotic dermatologic injury through the enzyme sphingomyelinase D.1 It is a public health problem in South America, especially in Argentina, Brazil, Chile, and Peru, where Loxosceles laeta is one of the most common spider and presumably the most toxic. The clinical picture may present as cutaneous loxoscelism or, less frequently, cutaneous-visceral or systemic loxoscelism.2 The latter may be ruled out after the first 24h.3 A 69-year-old male, who was attacked by a 3-cm brown spider, presented local pain and edema around the site of the bite after 14h (Fig. 1). The patient was put on corticosteroids and antihistaminics, but the lesion and the pain increased in following hours. The patient was referred to our hospital 3 days thereafter; at admission we observed an extensive purpuric plaque from left ribcage to the sternum region, irregular, with pale, congestive, and ecchymotic areas. At the upper end of the plaque, we observed a black crust of 1cm of diameter. It has not changed until the time of discharge at the 7th day of hospitalization and there were no other findings consistent with systemic damage. Cutaneous loxoscelism is a benign and self-limited injury, associated with edema and erythema after 6–8h. It usually produces areas of hemorrhage, vasoconstriction and ischemia around the bite called livedoid plaque, as shown in this case, but some of the victims progress to a necrotic ulcer.4 Therefore, loxoscelism should be closely monitored for its ability to produce cutaneous ulceration or to develop systemic involvement.
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.